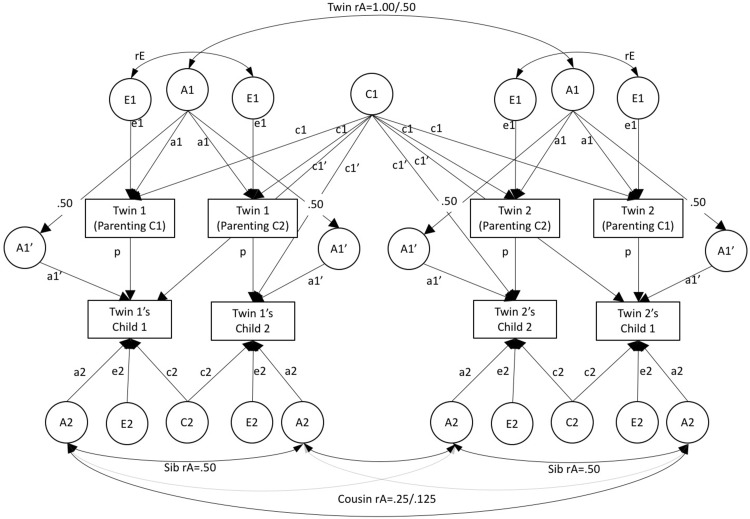
Fig. 3.
Multiple-children-of-twins structural equation model. Parent phenotype is variant across offspring (MCoT-var). Note: A1 = additive genetic effects on parental phenotype; C1 = shared-environmental effects on parental phenotype; E1 = nonshared environmental effects on parental phenotype; A1′ = genetic effects common to parental phenotype and offspring phenotype; C1′ = extended family effects whereby the shared environment of the parents influences offspring phjenotype; A2 = familial effects specific to offspring phenotype; C2 = shared-environmental effects on offspring phenotype (not estimable using cousin data); E2 = nonshared environmental effects on offspring phenotype; p = phenotypic effect of parent on offspring; rE = within-parent correlation between E1 for parenting of child 1 and 2. Allows parenting of each child to differ (when necessary this should be allowed to vary according to offspring zygosity). NB the pathway between A1 and A1′ is fixed to 0.50 because parents and children share 50% of their genome. To avoid over complicating path diagrams, variance paths have been omitted, but for all latent factors variance = 1. For A1′ this means that residual variance (after accounting for the path between A1 and A1′) is 0.75