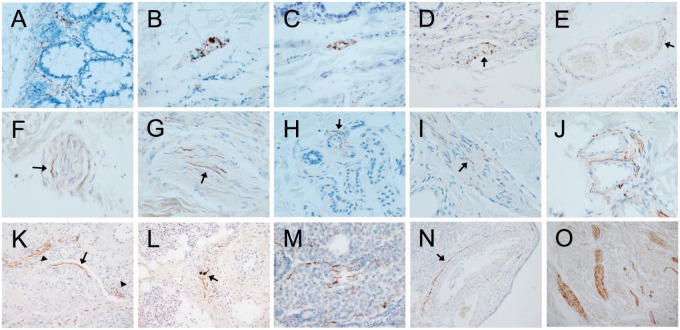
FIGURE 2.
Photomicrographs of autopsy sections immunohistochemically stained for pathological Asyn by the 2 compared methods illustrating common types of presumptively specific staining. Specific versus non-specific staining morphologies have been defined by their neuronal or non-neuronal appearance and empirically by their differential presence in normal control subjects versus subjects with autopsy-confirmed PD or other Lewy body diseases. Immunoperoxidase reaction product is brown, the counterstain is blue. Panels (A–E) are of sigmoid colon, (F–J) of skin from scalp, and (K–O) of submandibular gland. Most staining features were seen with both staining methods. (A) Several “beaded” fibers, consistent with axons, within the lamina propria (5C12 method). (B, C) Short fibers and puncta, the former consistent with axons, the latter consistent with presynaptic terminals or dystrophic neurites, within a ganglion of the submucosal plexus ([B] with the 5C12 method, [C] with the Nantes method). (D) Short perivascular fibers (arrow) and puncta, consistent with axons, within the submucosa (5C12 method). (E) Longer fiber, consistent with an axon, closely applied to the abluminal surface of a blood vessel within the submucosa (arrow; 5C12 method). (F, G) Fibers consistent with axons (arrows point to examples), within small nerve fascicles in the dermis ([F] with Nantes method, [G] with 5C12 method). (H) Fiber consistent with axon (arrow) applied to the ablumenal surface of a small blood vessel within a cluster of dermal sweat glands (5C12 method). (I) Fine fibers consistent with axons (arrow points to an example) on the surface of an arrector pili muscle in the dermis (5C12 method). (J) Multiple fibers applied to the ablumenal surfaces of dermal blood vessels; fibers running in parallel adjacent to 1 vessel are within a small nerve fascicle (5C12 method). (K) Long fibers (arrow) applied to the ablumenal surface of a blood vessel within the submandibular gland (Nantes method). Also seen are fibers running in parallel within a small nerve fascicle (arrowhead on left) and puncta presumptively representing cross-sectioned axons within a nerve fascicle (arrowhead on right). (L) Fibers running in parallel within a small submandibular gland nerve fascicle (Nantes method); 2 fibers have focal enlargements, consistent with dystrophic change (arrow). (M) Several fibers consistent with axons amongst serous epithelial cells (5C12 method). (N) Long fiber(s) closely applied to the ablumenal surface (arrow) of an arteriole within the submandibular gland (5C12 method). (O) Several large nerve fascicles within the stroma of the submandibular gland, each with numerous immunoperoxidase-stained fibers consistent with axons (5C12 method).