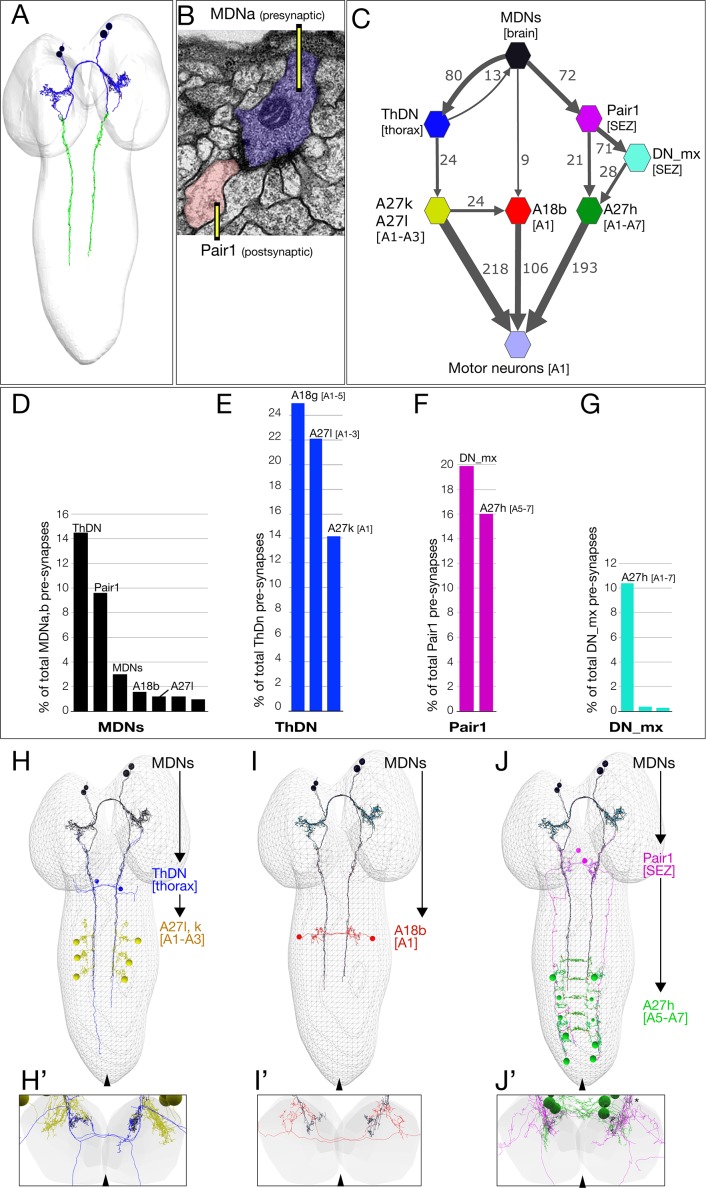
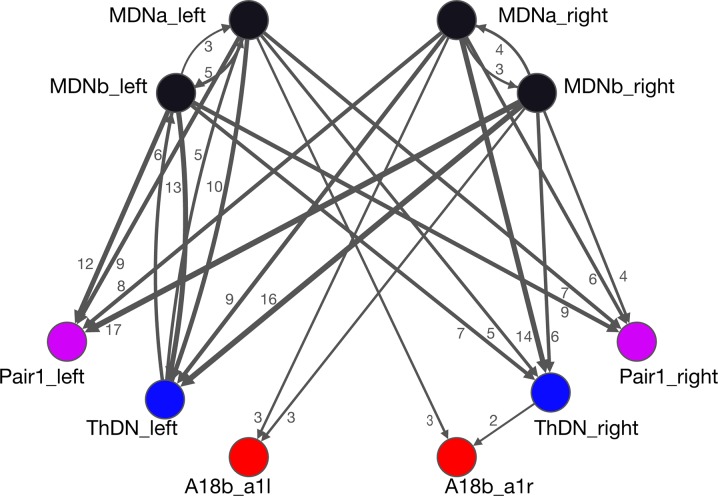
Figure 4. The MDN connectome: three pathways to distinct subsets of premotor neurons.
(A) TEM reconstruction of the bilateral MDNa,b neurons. Neuronal skeletons are colored to show post-synapses in the presumptive dendritic arbors of the brain (blue) and pre-synapses in the presumptive axonal descending process (green). Anterior, up. (B) Representative MDN output pre-synapse (blue) onto a post-synaptic Pair1 neuron (pink). (C) MDNs and their partners with the greatest number of synapses (synapse number shown next to connection arrows, and line width is proportional to synapse number). All connectivities are shown except unilateral synapses,<6 synapses, and the 15 synapses between MDNs. Each polygon represents pairs of the indicated neuron with the exception of these larger groups: A27k/A27l (six A27l neurons in A1-A3, four A27l neurons in A1-A2); A27h (14 neurons in A1-A7), and 30 pair of motor neurons in A1. This graph is provided as Supplementary file 1. json that can be opened in CATMAID. (D–G) Quantification of the percent of total pre-synapses that are targeted to the indicated neuron. All connectivities are shown except unilateral or <5 synapse connections. (H–J) The three MDN to premotor neuron pathways. (H) MDN-ThDN-A27l/k pathway. Only A27l is shown; A27k has a very similar morphology. (I) MDN-A18b pathway. (J) MDN-Pair1-A27h pathway. Dorsal view; anterior, up; midline, arrowhead. (H’–I’) Respective cross-sectional view of VNC neuropil (gray) and neurons in each pathway; note that synapses are primarily in the dorsal (motor) neuropil. Dorsal up, midline, arrowhead. Asterisk in J’ shows the approximate site of the synapse shown in panel B.