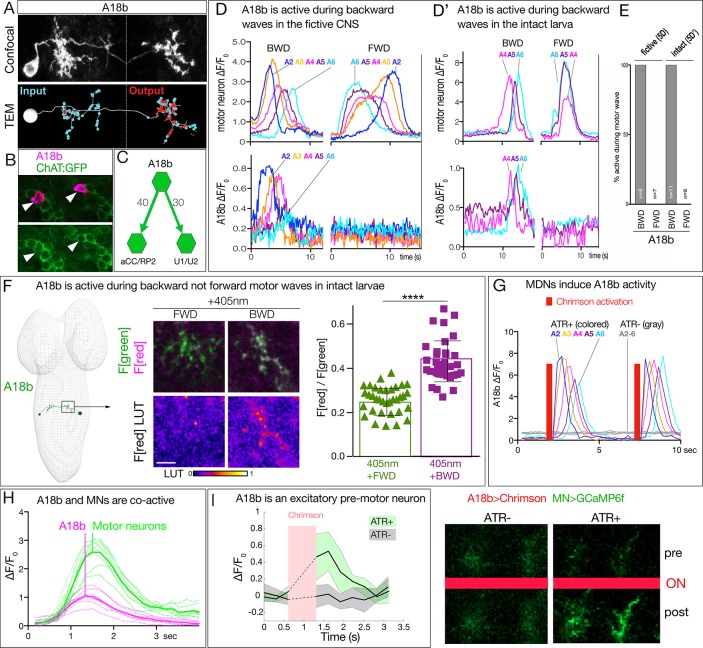
Figure 5. MDN activates the excitatory backward-active A18b premotor neuron.
(A) A18b morphology by light (MCFO) and electron microscopy (TEM). Top: Dorsal view of an individual A18b neuron in a second instar larval CNS by light microscopy (R94E10 > MCFO). Bottom: Dorsal view of an individual A18b neuron in a first instar larva in the TEM reconstruction. Cyan dots, post-synaptic sites; red dots, pre-synaptic sites. Anterior, up. Midline, dashed line. Genotype: R94E10-gal4 UAS-MCFO2. (B) A18b is cholinergic. A18b cell body (mCherry; magenta) and ChAT:GFP (green). Genotype: R94E10-Gal4, UAS-Chrimson:mCherry; mimic ChAT:GFP. (C) Connectivity of A18b to neurons with the greatest number of A18b post-synapses: the dorsal-projecting motor neurons aCC/RP2 and U1/U2 in segment A1. Synapse number shown. (D) In fictive preparations, A18b neurons are active in backward but not forward locomotion. ΔF/F0 of GCaMP6m in U1-U5 motor neurons (top) or jRCaMP1b in A18b (bottom) of five segments executing a forward (FWD) and then a backward (BWD) wave. This experiment was performed on eight different isolated third instar CNSs with similar results; quantified in E. Genotype: CQ-lexA/+; lexAop-GCaMP6m/R94E10-Gal4 UAS-jRCaMP1b.. (D’) In intact larvae, A18b neurons are active in backward but not forward locomotion. ΔF/F0 of GCaMP6m in motor neurons (top) and jRCaMP1b in A18b (bottom) in three segments. Times of BWD and FWD motor waves indicated. This experiment was performed on 19 waves (11 BWD, 8 FWD) in seven third instar larvae, all with similar results; quantified in E. Genotype: CQ-lexA/+; lexAop-GCaMP6m/R94E10-Gal4 UAS-jRCaMP1b.. (E) Quantification of data in panels D and E. BWD, backward waves; FWD, forward waves. (F) In intact larvae, A18b is preferentially active during backward not forward locomotion. CaMPARI in A18b neurites in a third instar larval CNS. Top, fluorescence emission (F) following 488 nm (green) or 561 nm (magenta) illumination; bottom, emission from 561 nm alone. Left, photoconversion (405 nm) during FWD or BWD locomotion. Right, quantification of red fluorescence over green fluorescence mean intensity. Each value represents data from an individual neurite. n = 35 for FWD and 36 for BWD. LUT, 561 nm emission intensity look up table. Scale bar, 10 μm. Genotype: R94E10-Gal4 UAS-CaMPARI. (G) In fictive preparations, MDNs activate A18b neurons, and induce backward A18b activity waves. Chrimson is expressed in MDN, and GCaMP6f in A18b. Red bars, time of 561 nm Chrimson activation. Colored traces indicate the ΔF/F0 of A18b GCaMP6f signal in 5 segments of an ATR +brain; gray traces are from ATR- animal. This experiment was performed on five different animals with similar results. Genotype: R49F02-Gal4AD/R94E10-lexA; R53F07-Gal4DBD/lexAop-GCaMP6f UAS-Chrimson:mCherry. (H) Dual color calcium imaging of jRCaMP1b in A18b (magenta) and GCaMP6m in U1-U5 motor neurons (green). In fictive preparations, A18b and motor neurons are co-active during backward waves. Both show similar initiation of activity, but A18b peak activity precedes motor neuron peak activity (vertical lines). Data are acquired every 168 ms from eight A18b/motor neuron pairs from three animals; peak activity of the motor neurons followed that of A18b by 0 ms (two pair), 168 ms (four pair), or 336 ms (two pair). Dashed lines, individual neurons; solid lines, average. Genotype: CQ-lexA/+; lexAop-GCaMP6m/R94E10-Gal4 UAS-jRCaMP1b.’. (I) A18b is an excitatory pre-motor neuron. A18b expresses Chrimson and aCC/RP2 motor neurons express GCaMP6f. Left: ΔF/F0 traces of GCaMP6f before and after 561 nm Chrimson activation (red bar) of three aCC/RP2 axons/dendrites within an animal. Solid bars represent means and shaded regions represent standard deviation from the mean (SDM). ATR +is shaded in green and ATR- in grey. Five animals were used in each group. GCaMP6f signal was not acquired during the Chrimson activation (dashed lines); t-test analysis for the first ΔF/F0 value after Chrimson activation between +ATR and -ATR showed significance (p=0.0071). Right: images of motor neuron GCaMP6f fluorescence pre- and post-Chrimson activation in ATR +and ATR- larvae. Genotype: 94E10-lexA/+; lexAop-Chrimson:mCherry/RRa-Gal4 UAS-GCaMP6f..