Fig. 2. Adenoviral overexpression of hepatic DEPTOR inhibits mTORC1 and improves hepatic steatosis in chronic-binge ethanol-fed mice.
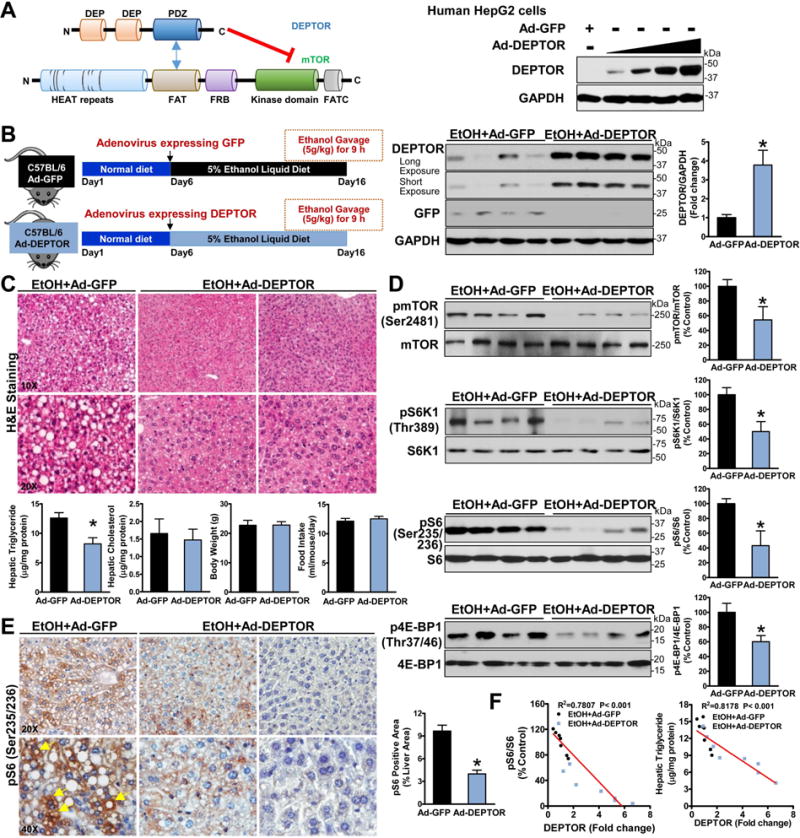
A. Schematic representation of the interaction regions between mTOR and DEPTOR. DEPTOR inhibits mTOR activity by binding the PDZ domain of DEPTOR to the FAT domain of the mTOR kinase. Immunoblotting analyses confirmed adenovirus-mediated overexpression of DEPTOR in human HepG2 cells. B. Hepatic overexpression of either DEPTOR protein (∼46 kDa) or GFP protein (∼27 kDa) in mice is confirmed. C. Overexpression of DEPTOR improves hepatic steatosis and lowers triglyceride accumulation in ethanol-fed mice. D. Overexpression of DEPTOR represses the induction of mTORC1 toward the downstream signaling in ethanol-fed mice. E. Positive staining for phosphorylated S6 in hepatocytes (yellow arrows) in ethanol-fed mice is reduced by overexpressing DEPTOR. F. Increased DEPTOR levels correlate with decreased S6 phosphorylation and lowered hepatic triglyceride content in mice. The data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 6–8. *P < 0.05 vs. ethanol-fed mice with Ad-GFP injection.
