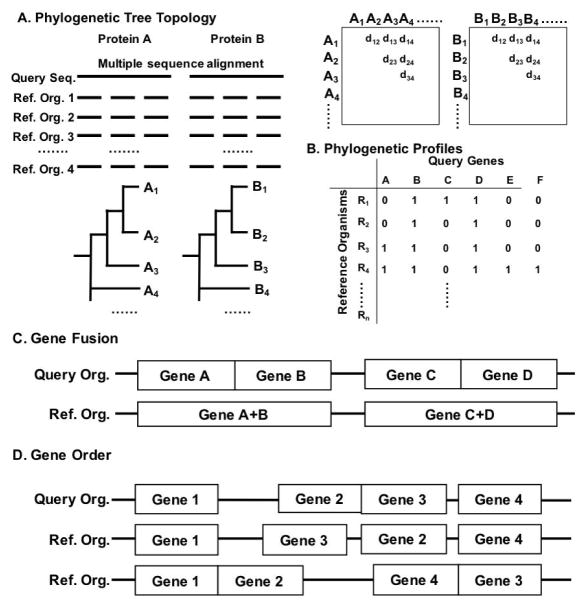
Figure 4. Comparative genomics-based methods.
A, Phylogenetic tree topology-based method. A pair of query sequences, A and B, are compared with n reference organisms and multiple sequence alignments are constructed. Based on the alignments, phylogenetic trees are computed, from which distances between all pairs of sequences are computed and stored in matrices. Then the similarity between two matrices is evaluated with a correlation coefficient. B, Phylogenetic profiles. Genes in a query organism is compared with n reference organisms by BLAST search. 1 represents the presence of the gene in the reference organism 0 for the absence. The table can also be filled with real-values, such as BLAST bit scores. C, Gene fusion. Two protein genes A and B are predicted as interacting if they fuse to form one protein gene AB in another organism. D, Gene order. If protein gene orders of proteins are conserved among different species, they are predicted as interacting proteins with each other.