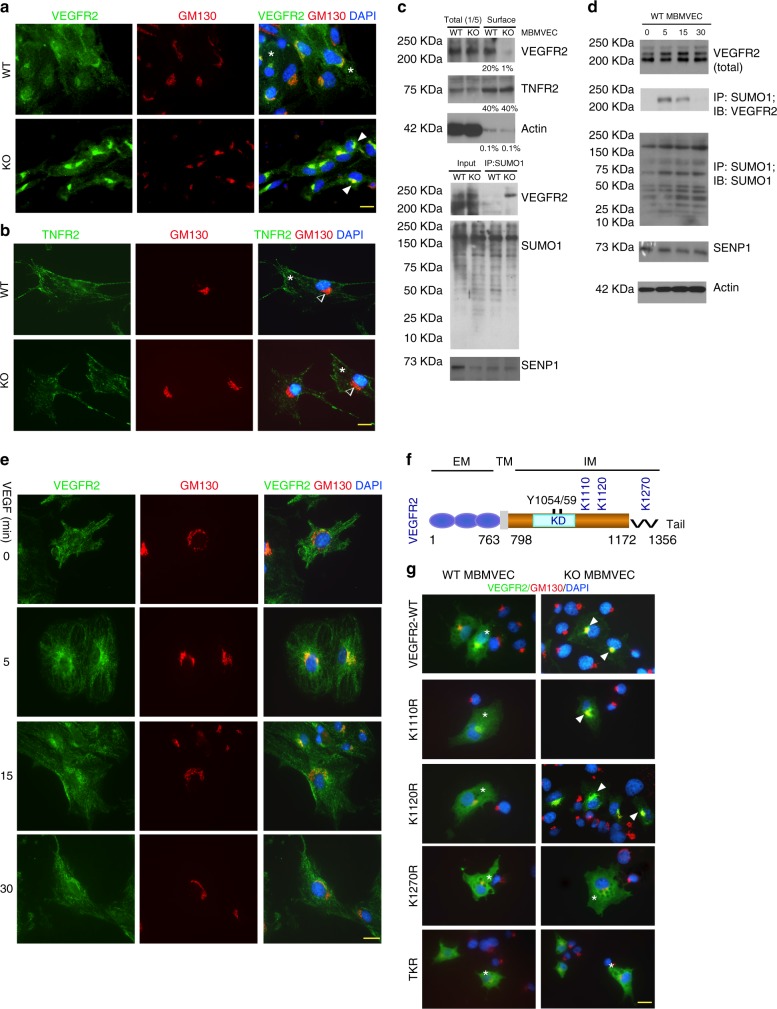
Fig. 4.
SUMOylation of VEGFR2 at the C-terminal lysine-1270 retains VEGFR2 in the Golgi. a, b. MBMVEC isolated from WT and SENP1-ECKO mice were subjected to immunofluorescence staining for VEGFR2 (a) or TNFR2 (b) together with a Golgi marker GM130. c WT and SENP1-ECKO MBMVECs were cultured in normal media. Cell-surface VEGFR2 was labeled by cell-surface biotinylation, and analyzed by streptavidin bead pull-down followed by western blotting with anti-VEGFR2. Percentage of cell-surface vs total proteins (VEGFR2, TNFR2 and actin) were quantified. n = 2. d Cell lysates of MBMVEC isolated from WT and SENP1-ECKO mice were subjected to western blot for total SENP1, VEGFR2, and co-immunoprecipitation assays for VEGFR2 SUMOylation. Relative molecular weights are shown on the left. e WT MBMVEC were treated with VEGF (10 ng/ml) for indicated times, and cells were subjected to immunofluorescence staining for co-localisation of VEGFR2 with GM130 (e). f Schematic diagram of VEGFR2 domains. EM: extracellular domain, TM: transmembrane domain, IM: intracellular domain, Tail: a flexible C-terminal segment (residues aa1172–1356). The numbers refer to the amino acid number, indicating the boundary of each domain. Y1054/59 located at the activation loop and putative SUMO sites within the IM (K1110, K1120, and K1270) are indicated. All VEGFR2 expression constructs are Flag-tagged at the N termini. g VEGFR2-WT and mutants were transfected into WT or SENP1-deficient MBMVEC. Co-localisation of VEGFR2 (anti-FLAG) with GM130 was determined. Merged images are shown (see Supplementary Fig. 6 for split channel images). A total of 10 cells from each group were analyzed. Golgi-accumulated VEGFR2 is indicated by arrows while membrane/cytosolic VEGFR2 by asterisks (a, b, e, g). TNFR2 was absent in Golgi (b). Three independent experiments were performed. Scale bar, 20 μm (a, b, e, g)