Fig. 8.
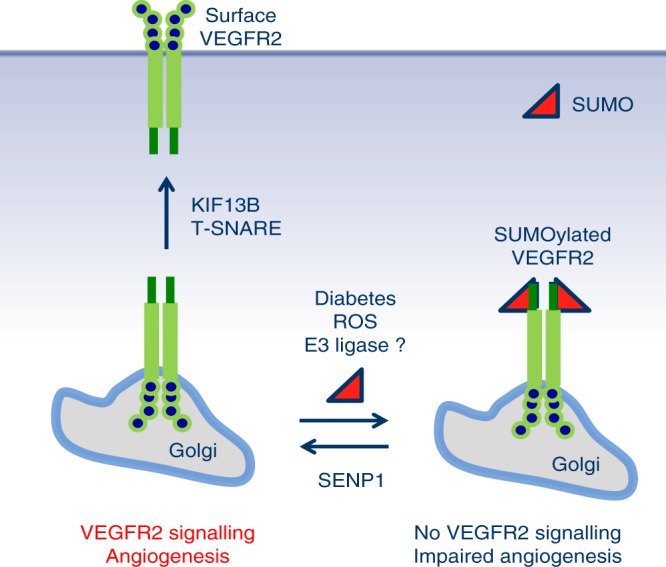
A model for SENP1-mediated VEGFR2 trafficking. SENP1 maintains VEGFR2 in an un-SUMOylated state, ensuring normal trafficking of VEGFR2 from ER/Golgi to plasma membrane in EC. We propose that a pool of VEGFR2 is constantly SUMOylated by an unidentified SUMO E3 ligase in resting EC or upon VEGF-engagement, and stored at the Golgi. Under pathological conditions such as ischemia, SENP1 expression is induced so that SUMOylated VEGFR2 can be rapidly deconjugated and transported to plasma membrane for strong angiogenesis response. Pathological conditions such as hyperglycemia and diabetes downregulate/inactivate SENP1, causing VEGFR2 hyper-SUMOylation and impaired angiogenic signalling as seen in SENP1-deficient EC (see text for details)
