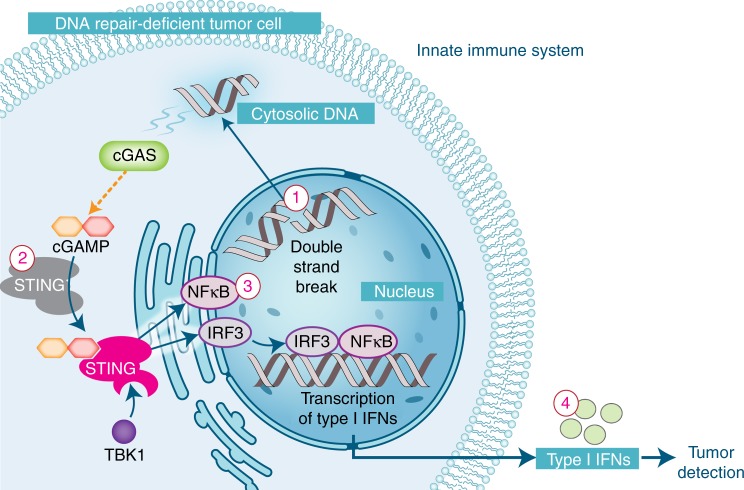
Fig. 4.
The STING hypothesis: activation of the innate immune system by DNA repair deficiencies in a DNA repair-deficient tumor cell. Cytosolic double-stranded DNA can be detected by cGAS which subsequently produces cGAMP (a cyclic dinucleotide), which in turn activates STING119. Upon activation, STING undergoes a conformational change, complexes with TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) and relocates to peri-nuclear region. There, TBK1 phosphorylates IRF3 and NFKB, which translocate to the nucleus and lead to the expression of immune-related genes, including type I interferons120