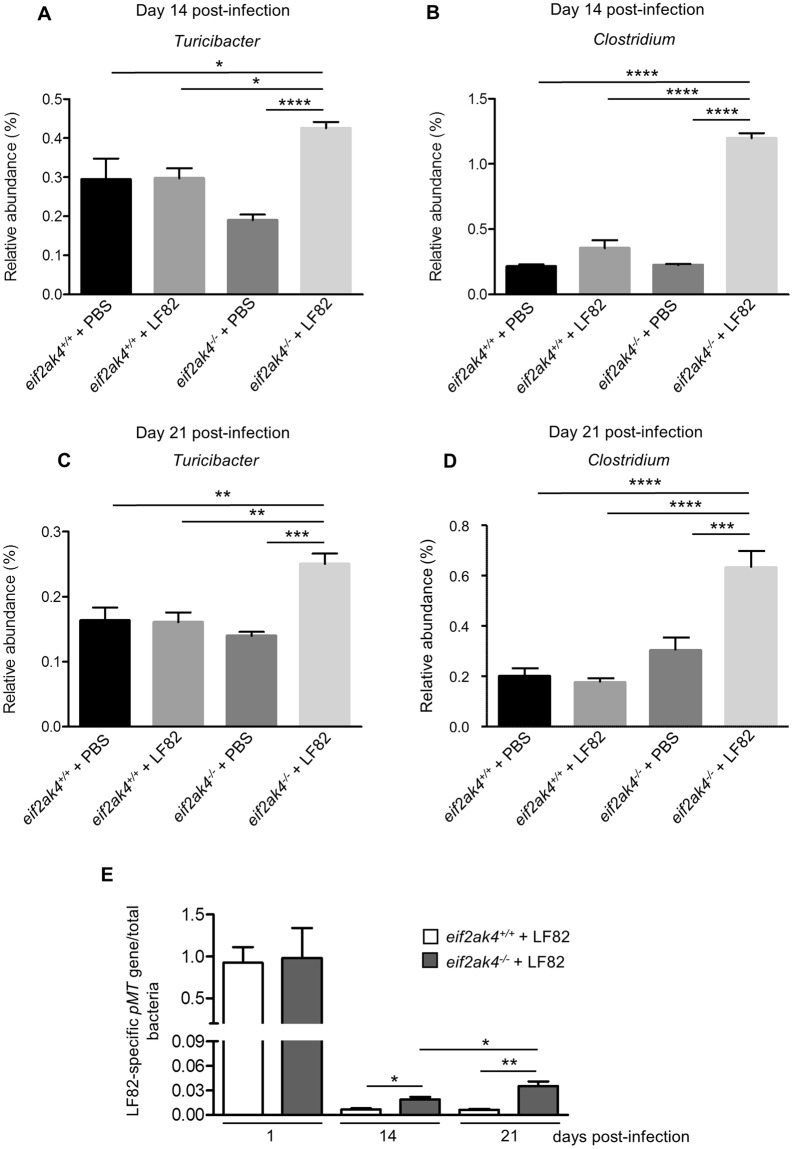
Figure 4.
Colonization of eif2ak4−/− mice with AIEC results in modification of Turicibacter and Clostridium abundance at day 14 and 21 post-infection. eif2ak4+/+ and eif2ak4−/− mice were challenged by oral gavage for 3 days (once per day) with PBS (N = 6 mice per group) or with 109 CFU of the AIEC LF82 strain (N = 7 mice per group). Feces were collected at day 14 (A,B) and 21 (C,D) post-infection for the analysis of the bacterial microbiota composition based on Illumina sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene. Relative abundance of Turicibacter (A,C) and Clostridium (B,D) between mouse groups: eif2ak4+/+ + PBS, eif2ak4+/+ + LF82, eif2ak4−/− + PBS and eif2ak4−/− + LF82. (E) qPCR analysis of the LF82-specific pMT gene expression level in the feces at the indicated time. Data were normalized to total bacterial. Fold-induction was calculated using the ΔΔCt method. Values were expressed as means ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA test followed by Bonferroni’s post-hoc comparisons. Ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; ****P ≤ 0.0001.