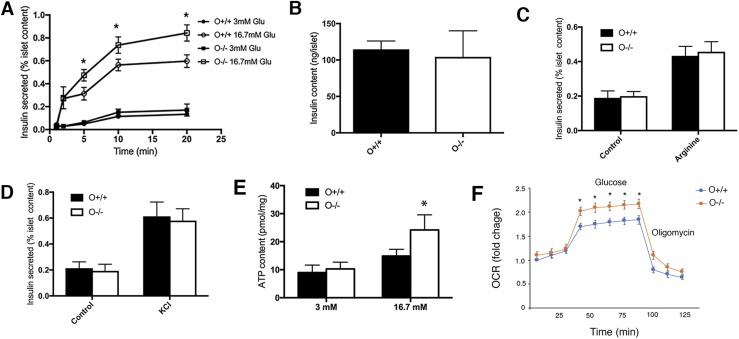
Figure 3.
Olfm4 deletion increases insulin secretion, ATP production, and mitochondrial respiration in islets isolated from Olfm4-deficient mice. (A) Secreted insulin levels in islets isolated from WT (O+/+) and Olfm4 homozygous-deficient (O−/−) mice in the presence of basal glucose (3 mM) and high glucose (16.7 mM). (B) Insulin content in islets isolated from WT and Olfm4-deficient mice subjected to glucose stimulation. Secreted insulin levels in islets isolated from WT (O+/+) and Olfm4 homozygous-deficient (O−/−) mice in the presence of (C) 10 mM arginine or (D) 35 mM KCl for 20 min. (E) ATP production in islets isolated from WT and Olfm4-deficient mice in the presence of basal glucose (3 mM) and high glucose (16.7 mM). (F) Mitochondria respiration reflected by OCR levels was detected in islets from WT (O+/+) and Olfm4-deficient mice (O−/−) under basal conditions or following the addition of glucose (20 mM) or oligomycin (1 µM). The results presented as fold change compared with basal level. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3). *P < 0.05 when compared with WT. Glu, glucose.