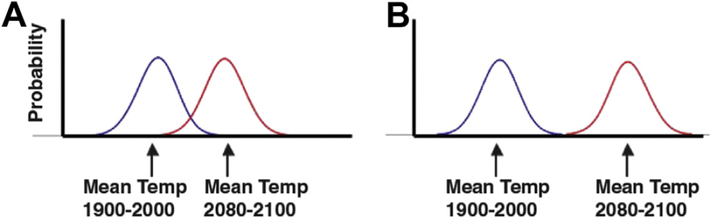
Figure 2.
Hypothetical distributions of summer season temperatures from 1900 to 2000 and 2080 to 2100. The x axis indicates seasonal temperature; the y axis, probability of occurrence (number of years in the century). (A) The highest growing-season temperature of the 20th century represents the median seasonal temperature by the end of the 21st century. (B) Future temperatures are out-of-bounds hot: that is, it is certain that the growing season temperature at the end of the 21st century will exceed the hottest growing season ever observed.44