Fig 3. Production and signaling of phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) oxidation after traumatic brain injury (TBI).
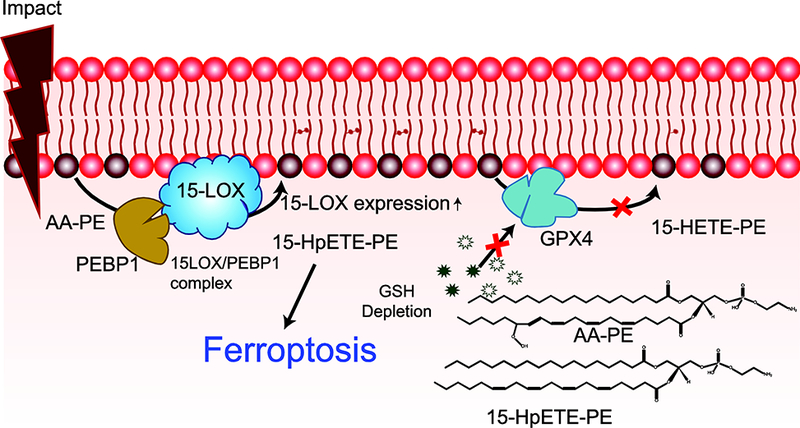
After TBI, the expression of 15-LOX and its formation of a complex with PE binding protein 1 (PEBP1) increase. This complex oxidizes arachidonyl (AA)-PE to 15-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid-PE (15-HpETE-PE). The glutathione (GSH) and glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) system responsible for the reduction of 15-HpETE-PE to 15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid-PE (15-HETE-PE) is ineffective post-TBI, resulting in 15-HpETE-PE accumulation and ferroptosis. Structure of AA-PE and 15-HpETE-PE are shown in inset.
