Figure 1.
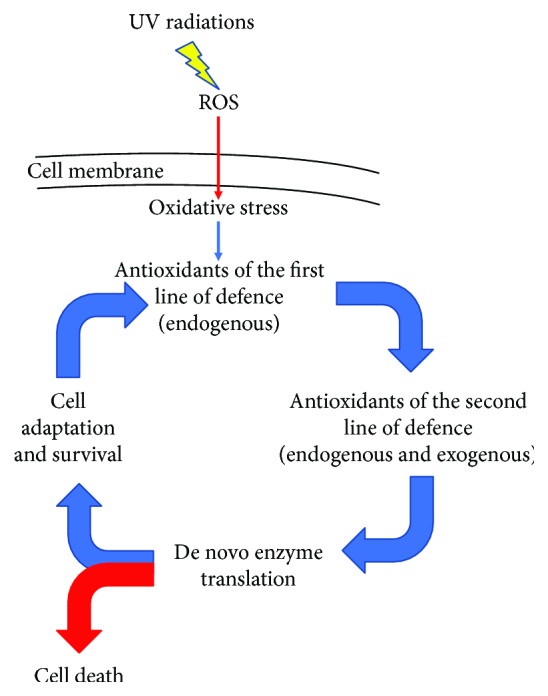
Schematic representation of the cell antioxidant response following oxidative stress injury. Upon UV radiations, ROS levels increase and oxidative stress is induced. Endogenous antioxidants suppress ROS formation and exogenous and endogenous antioxidants cooperate to suppress propagation reactions. Cell damages are repaired by de novo enzymes. Finally, if the cooperation among these antioxidant-related networks is able to counteract oxidative stress injury, the cell will survive after an adaptation process; otherwise, in case of prolonged or excessive stress, the cell will undergo cell death.
