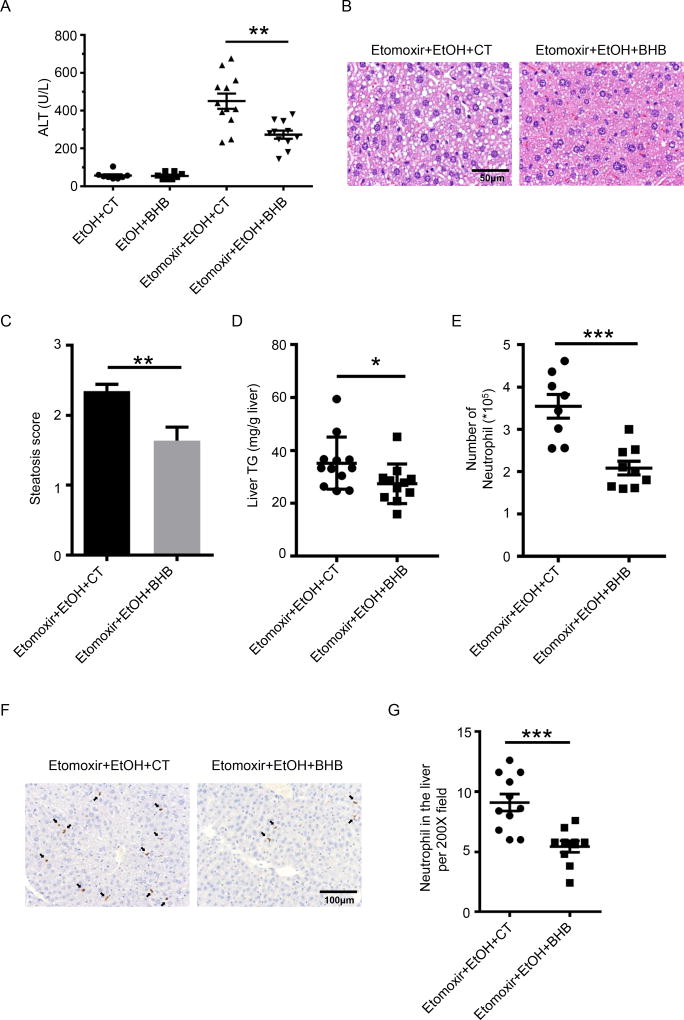
Fig. 2. BHB protected mice from etomoxir and ethanol induced liver injury.
(A–G) Mice were given an i.p. injection of BHB (3mmol/kg body weight) 6 hours after ethanol gavage and livers were collected 10 hours later. (A) Plasma ALT (n=8 per group for the EtOH gavage group with and without BHB; n=11~12 for the EtOH plus etomoxir group). (B) Representative liver histology. (C) Statistical analysis of steatosis scores (n=11~12 each group). (D) Statistical analysis of liver TG levels. (n=11~12 each group) (E) Statistical results of neutrophil (CD45+CD11b+Ly6G+) numbers in the liver (n=8~9 per group). (F) Representative images of Ly6B+ neutrophils in the liver. (G) Statistical analysis of Ly6B+ neutrophils in the liver by immunohistochemistry (n=10~11 per group). Data were analyzed with nonparametric Wilcoxon rank-sum tests.* P<0.05; ** P<0.01; ***P<0.001.