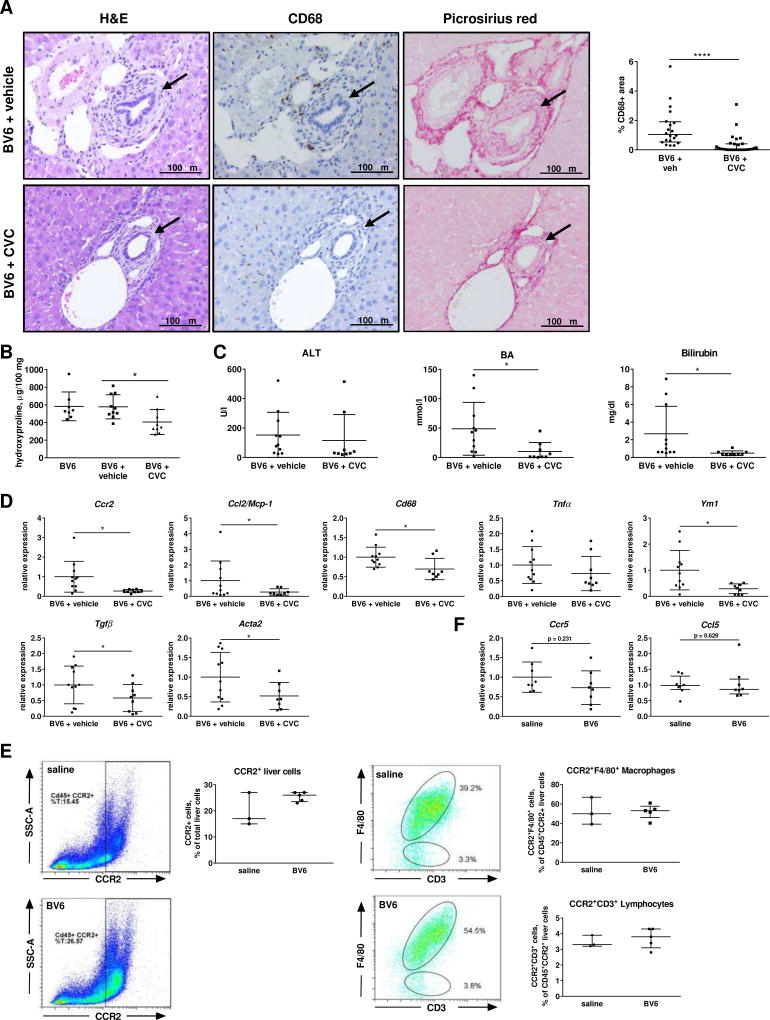
Fig. 6. Pharmacologic inhibition of CCR2-dependent monocyte recruitment attenuates biliary injury.
(A) Liver sections of BV6-injected mice (5 days) ± CVC or vehicle (20×). Arrows: bile ducts. pv: portal vein. Quantification of CD68+ cells on the right. (B) Liver hydroxyproline content. (C) Serum ALT, total BA and total bilirubin. (D) Macrophage infiltration and hepatic fibrosis markers by gene expression in whole livers. BV6 (n=8), BV6+vehicle (n=11), BV6+CVC (n=9). (E) Representative flow cytometric plots and quantification of CD45+CCR2+, CD45+CCR2+F4/80+ (macrophages) and CD45+CCR2+CD3+ (lymphocytes) liver cells. Saline (n=3); BV6 (n=5). (F) Ccr5 and Ccl5/Rantes gene expression. *p<0.05; **p<0.005 (Mann-Whitney).