Fig. 4.
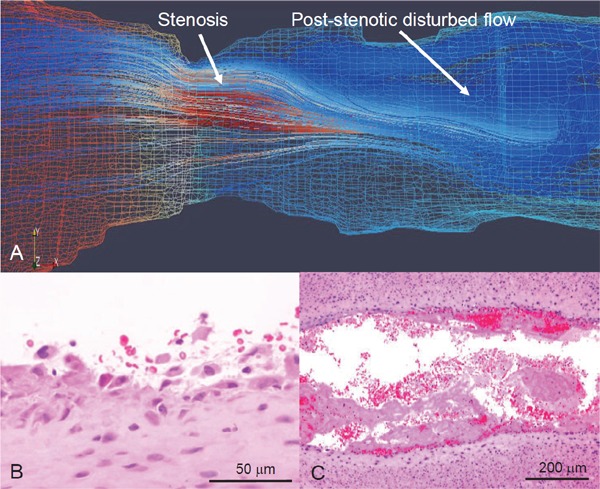
Computational flow simulation and microphotographs of erosive injury of rabbit stenotic femoral artery with SMC-rich plaque
Rabbit femoral arteries 3 weeks after balloon injury are constricted using a vascular occluder. (A) Representative computational reconstructed image and flow simulation in Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes model. Red and blue mesh indicates high and low pressure, respectively, on wall. Flow velocity in this model increases at stenosis and decreases at post-stenotic portion, resulting in disrupted flow. (B, C) Representative microphotographs of erosive injury and thrombus formation. Neointimal endothelial cells and SMCs are broadly detached at post-stenotic portion 15 minute after vascular stenosis (B) (Ref. 79, with permission). Large mural thrombi are formed at the portion 60 minute after vascular stenosis (C).
