FIGURE 1.
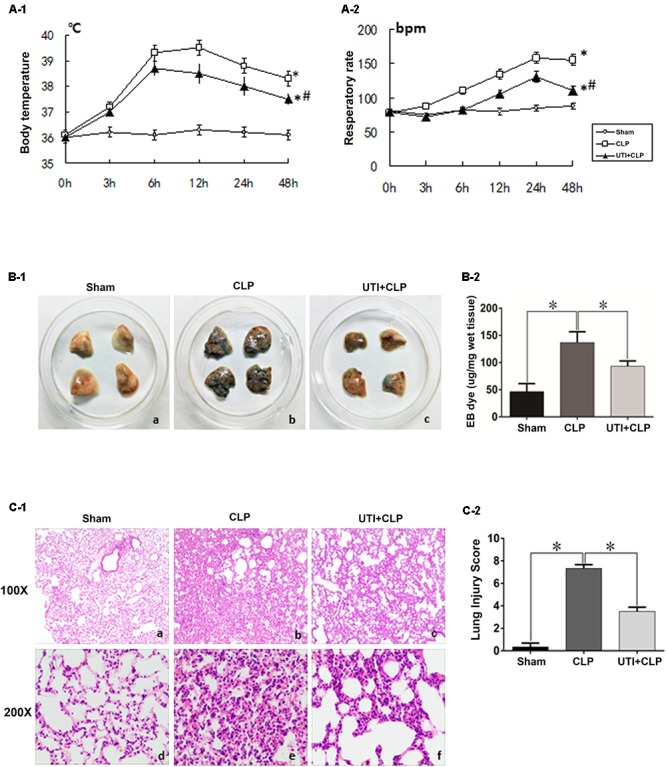
Clinical manifestations and histological assessment of the effects of urinary trypsin inhibitor (UTI) on cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced sepsis rats. The temperature and respiratory rate of rats in both CLP and UTI+CLP groups showed a significantly higher level in comparison with the sham group at 48 h (∗A-1 p = 0.000 and 0.0001, respectively; ∗A-2 p = 0.000 and 0.000, respectively). Note that both readings were markedly decreased in UTI+CLP group compared with CLP group (#A-1 p = 0.015 and #A-2 p = 0.001). The lung tissues from the sham group exhibited a normal color (B-1a) and gross features. There were detectable histopathological changes (C-1a,d). In the CLP group, EB inundated the lung tissue (B-1b) (p = 0.000). In hematoxylin and eosin stained sections, severe pulmonary edema, hemorrhage in the stroma, alveolar collapse, and mass inflammatory cell infiltration were evident (C-1b,e) along with high lung injury score compared with the CLP group (LIC) (C-2) (p = 0.000). The extravasated EB in the UTI+CLP group was noticeably reduced compared with CLP group (B-1c,B-2) (p = 0.025). The UTI+CLP group showed a lesser destruction of lung structure (C-1c,f) compared with the CLP group. Furthermore, it showed a lower lung injury score than the CLP group (C-2) (p = 0.001). All values represent mean ± SD in triplicate; ∗ and # represents p < 0.05.
