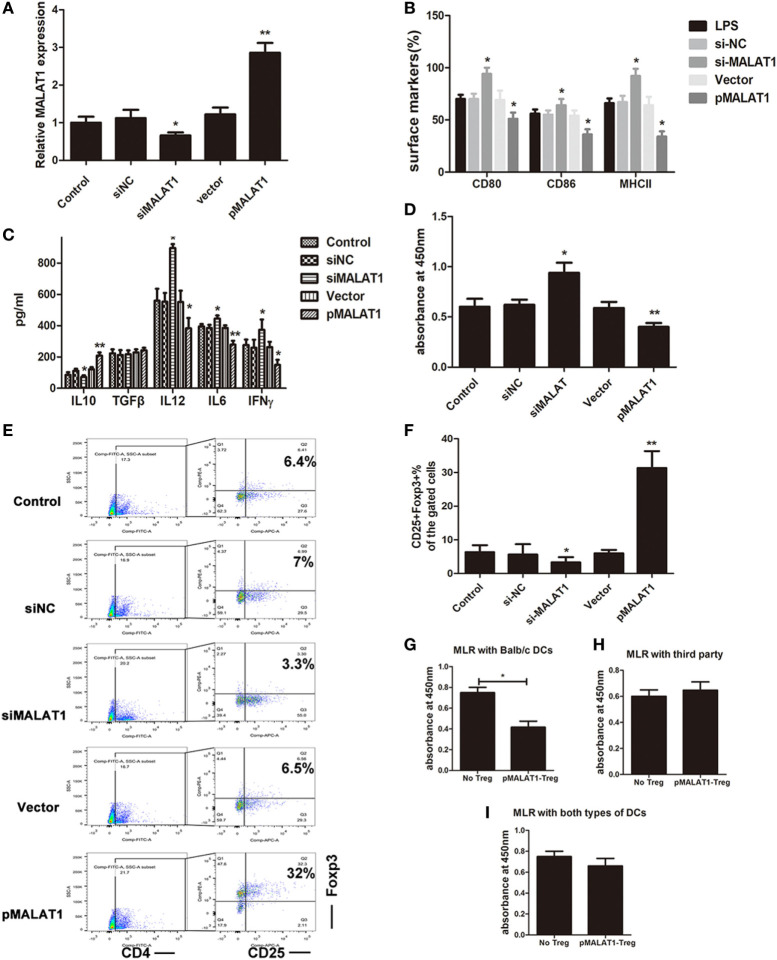
Figure 2.
Ectopic MALAT1 favors tolerogenic dendritic cells (tDCs) by inducing T cell hyporesponsiveness and Tregs expansion. Dendritic cells (DCs) were transfected with a MALAT1 pcDNA3.1 vector (pMALAT1, 2.5 µg/ml), a control vector (Vector, 0.625 µg/ml), MALAT1 siRNA (siMALAT1, 100 nM), or siRNA control (siNC, 25 nM) for 6 h before LPS treatment. (A) The expression of MALAT1 was confirmed by quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR in DCs receiving the different treatments. Expression of MALAT1 was effectively upregulated by pMALAT1, whereas MALAT1 siRNA suppressed MALAT1 expression in DCs. (B) Expression of the costimulatory markers CD80, CD86, and MHCII was analyzed by flow cytometry and is shown as the percentage of CD11c+ cells. MALAT1-suppressed DCs displayed increases in CD80, CD86, and MHCII expression levels compared with those of control DCs treated with LPS. (C) The cytokine secretion levels of IL10, TGFβ, IL12, IFNγ, and IL6 in the DC supernatants were analyzed by ELISA. The induced expression of MALAT1 in LPS-stimulated DCs resulted in reduced levels of IL6, IL12, and IFNγ, whereas levels of IL10 were significantly increased, but no significant effect was observed on TGF-β. (D) DC-triggered T cell proliferation was evaluated by BrdU-ELISA. For this, DCs were treated with mitomycin C (10 mg/ml, 2 h) and cocultured with allogeneic T cells for 48 h at a DC:T cell ratio of 1:20. T cells cocultured with MALAT1-overexpressing DCs exhibited reduced proliferative ability compared with those cocultured with LPS-DCs. (E,F) In the cocultured T cells, the numbers of Tregs (CD4+, CD25+, and Foxp3+) cells were assessed by flow cytometry. Boxes depict gates and numbers correspond to the percentage of cells in each gate. The data are shown with a representative flow cytometry (E) and the percentages (F). The number of Tregs was significantly increased when T cells were cocultured with MALAT1-overexpressing DCs compared with LPS-DCs. (G–I) Tregs (CD4+CD25+) isolated from T cells cocultured with pMALAT1-conditioned DCs by MACS were added into coculture with DCs (from BALB/c, third-party mice or both types ratio of 1:1) and T cells, with a Treg:T cell:DC ratio of 10:10:1. Then, the suppressive ability of the Tregs was assessed by T cell proliferation assays using BrdU-ELISA. Tregs derived from MALAT1-overexpressing DC (from BALB/c mice) cocultures suppressed T cell proliferation in the presence of BALB/c DCs as stimulators but not in the presence of DCs from third-party mice, whereas there was no significant difference in T cell proliferation between both types of LPS-induced DCs. The data are presented as the mean ± SD from at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. pMALAT1-Treg, Tregs induced by pMALAT1-conditioned DCs in MLRs; No-Treg, without Tregs.