Figure 2.
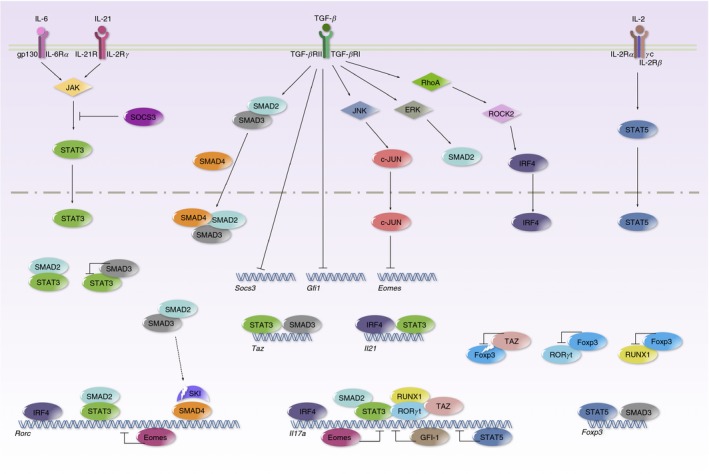
Transforming growth factor‐β (TGF‐β) promotes T helper 17 (Th17) differentiation through multiple mechanisms. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), induced by interleukin‐6 (IL‐6) or IL‐21, potentiates the Th17‐related transcriptional programme by binding to Rorc, Il17a, and Il21 loci. TGF‐β receptor signalling phosphorylates SMAD2 and SMAD3. The SMAD2/3 complex interacts with SMAD4 and translocates into the nucleus. Meanwhile, SMAD2 and SMAD3 act as a co‐activator and co‐repressor of STAT3, and oppositely modify STAT3‐induced transcription. TGF‐β signalling triggers SKI degradation to unleash SMAD4 and SKI complex repressed ROR γt expression. TGF‐β suppresses SOCS3 to prolong STAT3 activation. TGF‐β suppresses GFI‐1 to promote Il17a transcription. TGF‐β suppresses Eomes through the JNK‐c–JUN pathway to enhance Rorc and Il17a transcription. TGF‐β drives RhoA‐ROCK2 to phosphorylate IRF4 and to up‐regulate the expression of ROR γt, IL‐17 and IL‐21. TGF‐β induces TAZ to co‐activate ROR γt and to reduce Foxp3 through proteasomal degradation.
