Figure 7.
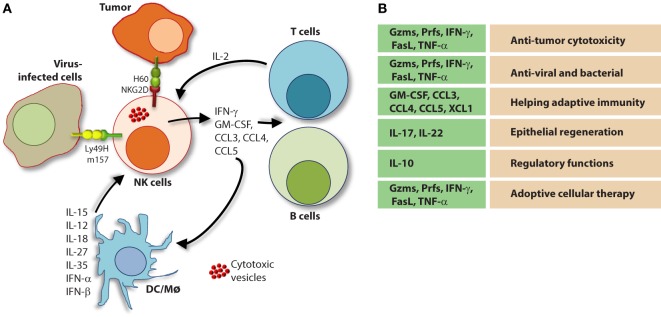
Role of a “third signal” in natural killer (NK) cell activation. (A) A brief description of the significant interactions between NK and myeloid cells. NK cells possess inherent abilities to mediate cytotoxicity and produce inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Myeloid cell-derived cytokines play a central role in regulating the effector functions of NK cells. Interactions between the innate NK cells and the primary arms of the adaptive immunity (T and B cells) are less explored. Stimulation through activation receptors (i.e., NKG2D or Ly49H) help recognize tumor (H60) or infected target cells (murine cytomegalovirus-derived m157). (B) A summary of major soluble factors produced by NK cells and their intended functions.