Figure 1.
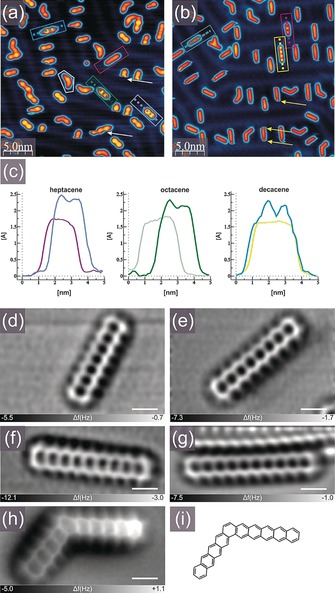
On‐surface generation of higher acenes. a,b) Empty state STM images of the Au(111) surface partially covered with a) hydrogen‐protected acene precursors 1 a, 1 b, and 1 d, and kinked isomer 1 d′, and b) heptacene (2), octacene (3), decacene (5) and kinked decacene isomer (5′). Precursor molecules are easily discernible by the presence of two pronounced lobes corresponding to two non‐aromatic rings each containing two methylene groups, exemplary precursors are marked by rectangles: 1 a—violet, 1 b—green, 1 d—blue. Parent acenes in (b) are indicated by rectangles: 2—purple, 3—gray, 5—yellow. Dashed lines in (a) and (b) indicate directions of profile lines shown in (c). After deposition a small fraction of molecules could be found already partially (white contour) or very rarely completely dehydrogenated (red rectangle). White and yellow arrows in (a) and (b) indicate the typical displacement of precursors and frustrated motion of acenes during STM imaging, respectively. Tunneling current 30 pA, bias voltage +2.0 V. c) Profile lines along precursor molecules and parent acenes showing a difference in their STM appearance and evidencing the presence of two pronounced lobes in the topographies of the precursors. d–h) Laplace filtered constant height, frequency shift nc‐AFM images of 2 (d), 3 (e), 4 (f),27 5 (g), and 5′ (h) generated by annealing, scale bar: 5 Å. i) Structural scheme of 5′.
