Figure 11.
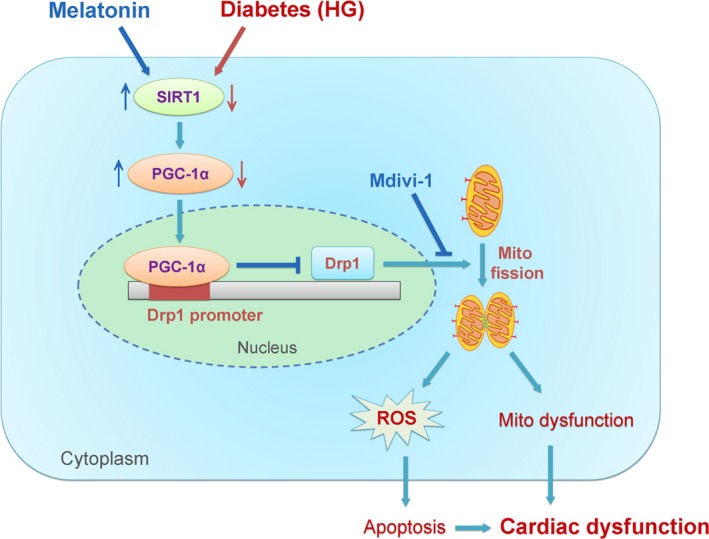
Schematic figure illustrating that melatonin prevents against diabetes‐induced mitochondrial fission and cardiac dysfunction through SIRT1‐PGC‐1α‐Drp1 pathway. SIRT1 positively regulates the expression of PGC‐1α, which negatively regulates the expression of Drp1 directly by binding to its promoter. Diabetes (hyperglycemia, HG) reduced the expression of SIRT1 and PGC‐1α (red arrows) and then increased the expression of Drp1. Drp1 triggers mitochondrial fission and subsequently leads to mitochondria‐derived ROS production and mitochondrial dysfunction, which results in the development of cardiac dysfunction. Treatment with melatonin increased the expression of SIRT1 and PGC‐1α (blue arrows) and then prevented Drp1‐mediated mitochondrial fission. Mdivi‐1 prevented diabetes‐induced mitochondrial fission by inhibiting Drp1 activity. As a result, melatonin or mdivi‐1 suppressed mitochondria‐derived ROS production, alleviated mitochondrial dysfunction, reduced cell apoptosis, and protected against diabetes‐induced cardiac dysfunction. Mito, mitochondrial; ROS, reactive oxygen species
