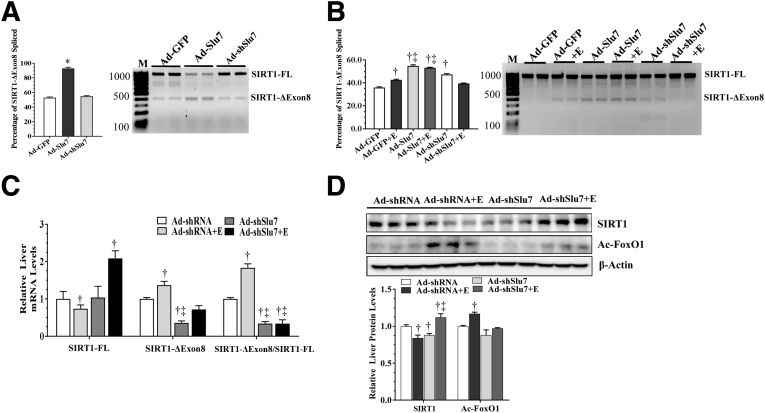
Figure 2.
Ad-mediated knockdown of hepatic Slu7 regulates hepatic sirtuin (SIRT) 1 pre-mRNA splicing in mice after ethanol administration. A: Mouse AML-12 hepatocytes were infected with Ad-GFP, Ad-Slu7, and Ad-shSlu7. Relative abundance of SIRT1-ΔExon8 or SIRT1 full length (SIRT1-FL). B: Female C57BL/6J mice were pair fed either a control diet or an ethanol (E)–containing diet for 10 days, followed by single gavage of ethanol. During the 10-day chronic-plus-binge ethanol feeding period, Ad-shSlu7 or Ad-shRNA control (0.5 to 1.0 × 109 active viral particles in 200 μL of phosphate-buffered saline) was given to mice twice on days 1 and 5. Relative abundance of SIRT1-ΔExon8 or SIRT1-FL. C: Relative liver mRNA levels of SIRT1-FL and SIRT1-ΔExon8 and ratio of SIRT1-ΔExon8/SIRT1-FL. D: Western blot analysis of liver SIRT1 and acetylated (Ac) forkhead box protein O (FoxO) 1 (on separate gels). Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 3 replications (A and B); n = 5 to 12 mice (C and D). ∗P < 0.05 versus Ad-GFP controls; †P < 0.05 versus pair-fed Ad-shRNA controls; ‡P < 0.05 versus ethanol-fed Ad-shRNA. M, markers.