Figure 5.
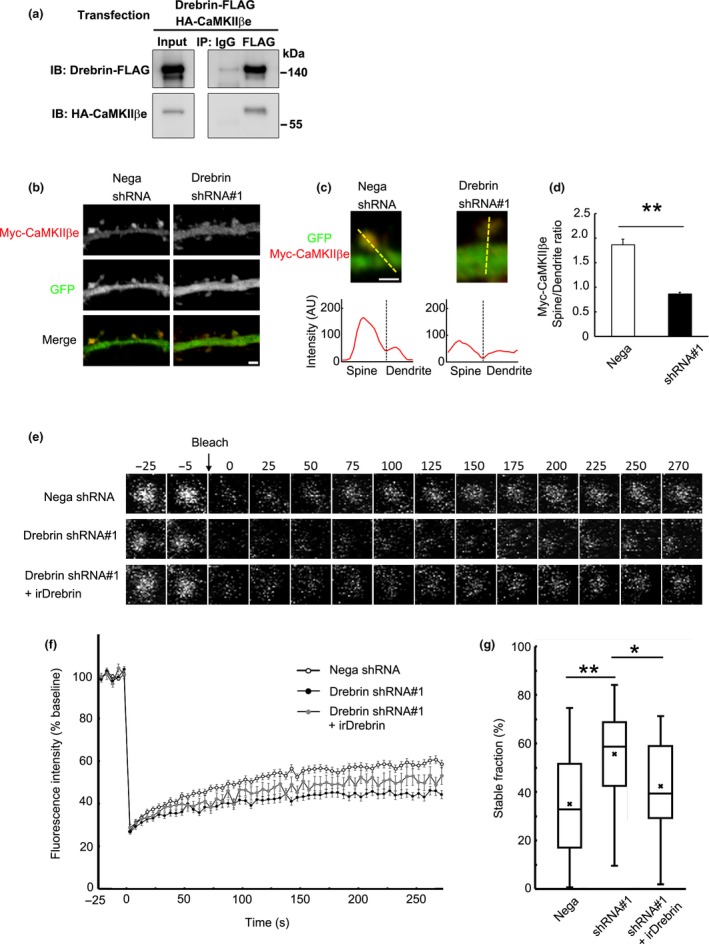
Spine localization of non‐F‐actin binding isoform CaMKIIβe depends on drebrin. (a) Coimmunoprecipitation between CaMKIIβe and drebrin. HEK293 cells were transfected with Drebrin‐FLAG and HA‐CaMKIIβe. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti‐FLAG antibody. (b) Cultured neurons were transfected with Myc‐CaMKIIβe + negative shRNA (control) or drebrin shRNA#1. Immunofluorescence intensities of Myc‐CaMKIIβe were measured in spines and parent dendrites. Scale bars, 2 μm. (c) Enlarged images of the dendritic spine of control and drebrin‐KD neurons. The line scans show Myc‐CaMKIIβe pixel intensities across the spine and dendrite. Scale bar, 1 μm. (d) Quantifications of the intensity ratio (spine:dendrite) of CaMKIIβe. Data are presented as means ± SEM (n = 24 neurons for negative shRNA, and n = 29 neurons for drebrin shRNA#1, **p < 0.01, Welch's t‐test). (e) FRAP analysis of GFP‐CaMKIIβe. Cultured neurons were transfected with GFP‐CaMKIIβe + negative shRNA, drebrin shRNA#1, or drebrin shRNA#1 + RNAi‐resistant drebrin (irDrebrin). Live confocal images of GFP‐CaMKIIβe were captured every 5 s for 300 s. (f) FRAP curves of GFP‐CaMKIIβe in each condition. (g) Quantification of the stable fractions. Box plots show the mean, median, interquartiles, and range (n = 80 spines for negative shRNA, n = 34 spines for drebrin shRNA#1, and n = 22 spines for drebrin shRNA#1+ irDrebrin, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, one‐way anova with Steel–Dwass post hoc test).
