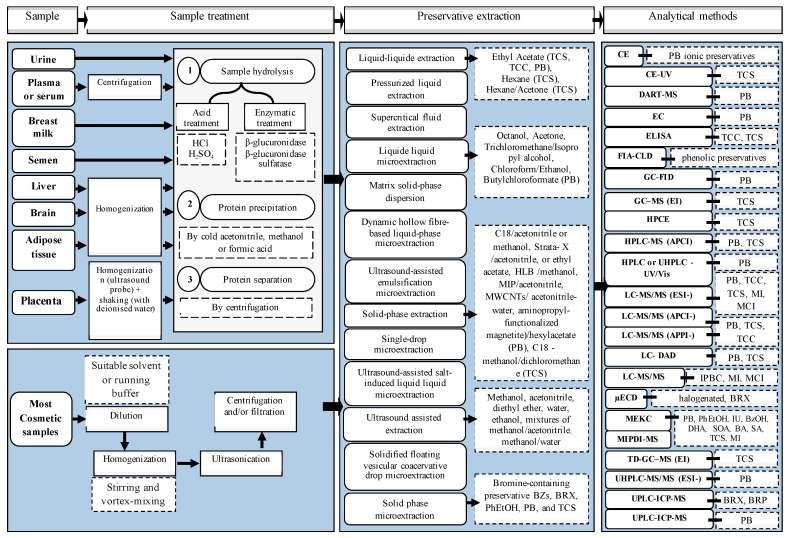
Figure 4.
Steps followed in the analysis of cosmetic preservatives from the sample treatment to the analytical methods [137,159,160] where: µECD: microelectron capture detector; APCI: atmospheric pressure chemical ionization; APPI: atmospheric pressure photoionization; BA: benzoic acid; BRP: bronopol; BRX: bronidox; BzOH: benzyl alcohol; BZs: benzoates other than sodium benzoate; CE: capillary electrophoresis; CLD: chemiluminescent detection; DAD: photodiode array detection; DART: direct-analysis-in-real-time; DHA: dehydroacetic acid; EC (D): electrochemical (detector); EI: electron impact; ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; ESI: electrospray ionization; FIA: flow injection analysis; FID: flame-ionization detector; GC: gas chromatography; HLB: divinylbenzene/n-vinylpyrrolidone copolymer; HPCE: high-performance capillary electrophoresis; HPLC: high-performance liquid chromatography; ICP: inductively-coupled plasma; IPBC: iodopropynyl butylcarbamate; IU: imidazolidinyl urea; LC: liquid chromatography; MCI: methylchloroisothiazolinone; MEKC: micellar electrokinetic chromatography; MI: methylisothiazolinone; MIP: molecular imprinted polymer; MIPDI: microwave-induced plasma desorption ionization; MS: mass spectrometry; MWCNTs: multi-walled carbon nanotubes; PB: parabens; PhEtOH: phenoxyethanol; SA: salicylic acid; SOA: sorbic acid; TCC: triclocarban; TCS: triclosan; TD: thermal desorption; UHPLC: ultra-high performance liquid chromatography; UPLC: ultra-performance liquid chromatography; UV: ultraviolet; UV–VIS: ultraviolet–visible.