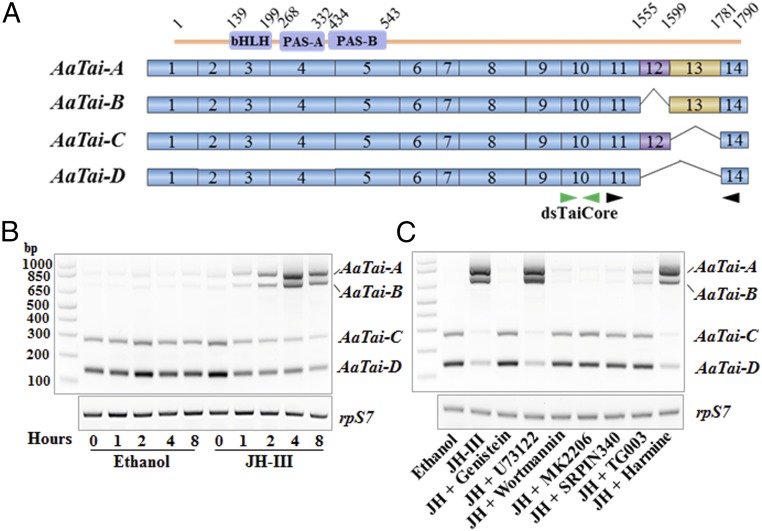
Fig. 2.
JH regulates the splicing of A. aegypti taiman. (A) Scheme of the AaTai isoforms. The constitutive exons are shown as solid blue boxes. E12 (purple) and E13 (orange) are alternatively spliced in the isoforms. The bHLH, PAS-A, and PAS-B domains are located in the N-terminal end of AaTai proteins. Green arrows point to the region where dsRNA was designed to knock down all AaTai isoforms. Black arrows indicate the locations of the primers used in RT-PCR. (B) JH induces the inclusion of E13 to produce the isoforms AaTai-A and AaTai-B. Fat bodies from female mosquitoes at 30 min PE were cultured in vitro in the presence of JH-III (1 μM). The mRNA levels of individual AaTai isoforms were assessed using RT-PCR with the primers shown in A. The RpS7 gene was used as an internal control. (C) RTK/PI3K/Akt pathway is required for the JH-regulated alternative splicing of AaTai. In vitro-cultured fat bodies were preincubated with genistein, U73122, wortmannin, MK2206, SRPIN340, TG003, or harmine for 1 h, followed by incubation with JH-III (1 μM) for 4 h.