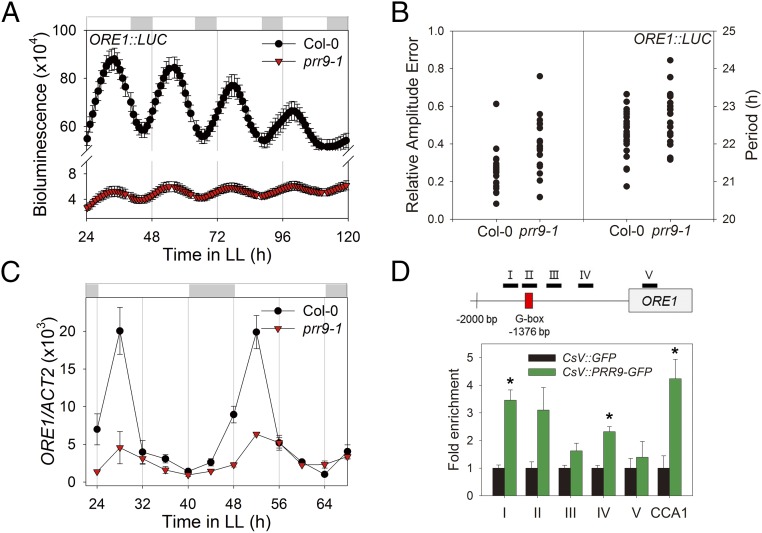
Fig. 4.
ORE1 is directly regulated by PRR9, a core clock component. (A) ORE1 promoter activity under LL in Col-0 and the prr9-1 mutant. Luminescence intensity from ORE1:LUC in excised leaves (mean ± SEM, n = 24). (B) Relative amplitude error (RAE; a measure of the strength of rhythmicity, where RAE = 0 for a perfect sine wave and RAE = 1.0 defines the limit of a statistically significant oscillation) of ORE1:LUC in Col-0 and prr9-1 mutant was analyzed by fast Fourier transform-nonlinear least-squares (FTT-NLLS) analysis (Left, n = 24). Period lengths of ORE1:LUC were computed from an experiment in Col-0 and prr9-1 (Right). (C) mRNA abundance of ORE1 in Col-0 and prr9-1 (mean ± SEM, n = 3). ACT2, internal control. (D) ORE1 promoter binding affinity of PRR9 in a CsV:PRR9-GFP transgenic line. Diagram for the ORE1 amplicons (I–V) in ChIP assay are indicated. Red box indicates G box (CACGTG). Two-week-old seedlings were harvested 4 h after lights on. The fold enrichment is a ratio of CsV:PRR9-GFP normalized to CsV:GFP plants. The binding of PRR9-GFP to the CCA1 promoter is used as a positive control (mean ± SEM, n = 3). Asterisk indicate statistically significant difference from CsV:GFP (t test, *P < 0.05).