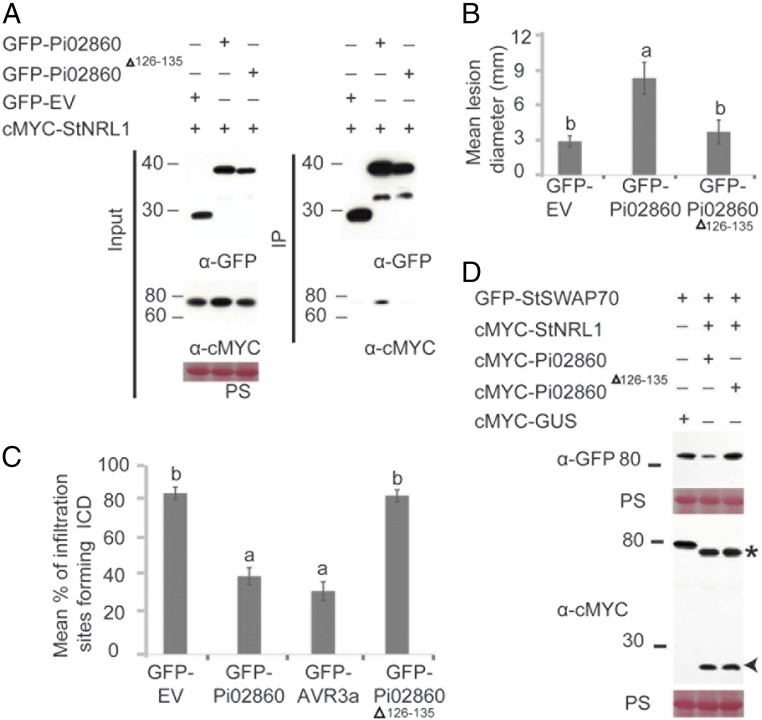
Fig. 5.
A Pi02860 mutant fails to interact with NRL1 or promote StSWAP70 degradation. (A) IP of protein extracts from N. benthamiana leaves transiently expressing cMYC-StNRL1 with either GFP-EV, GFP-Pi02860, or GFP-Pi02860Δ126–135 using GFP-Trap confirmed that cMYC-StNRL1 associates with GFP-Pi02860 but not with GFP-Pi02860Δ126–135. IP was analyzed by immunoblotting using an anti-GFP antibody showing protein fusions GFP-Pi02860, GFP-Pi02860Δ126–135, GFP-EV, and the anti-cMYC antibody showing protein fusions of cMYC-StNRL1 of the expected size. (B) Expression of wild-type GFP-Pi02860 significantly enhances P. infestans infection compared with the control GFP-EV. However, the Pi02860Δ126–135 fails to enhance P. infestans colonization. The results shown are combinations of three individual biological replicates (ANOVA, P < 0.001; n = 75 per construct) and error bars show SE. Letters on the graph denote statistically significant differences. (C) Suppression of ICD by Pi02860Δ126–135 is significantly reduced (P < 0.001, n = 45). The graph shows the mean percentage of infiltration sites forming ICD by transient expression of INF1 with GFP-EV, GFP-Pi02860, GFP-PiAvr3a, or GFP-Pi02860Δ126–135. The graph represents the combined data from three biological replicates. Letters on the graph denote statistically significant differences and error bars show SE. (D) The Pi02860Δ126–135 mutant fails to degrade StSWAP70 by StNRL1. GFP-StSWAP70 and cMYC-StNRL1 were transiently coexpressed with either wild-type cMYC-Pi02860 or mutant cMYC-Pi02860Δ126–135 in N. benthamiana leaves. Immunoblots with anti-GFP show the protein fusion of GFP-StSWAP70; the anti-cMYC antibody shows protein fusion of cMYC-Pi02860 and cMYC-Pi02860Δ126–135 of the expected size.