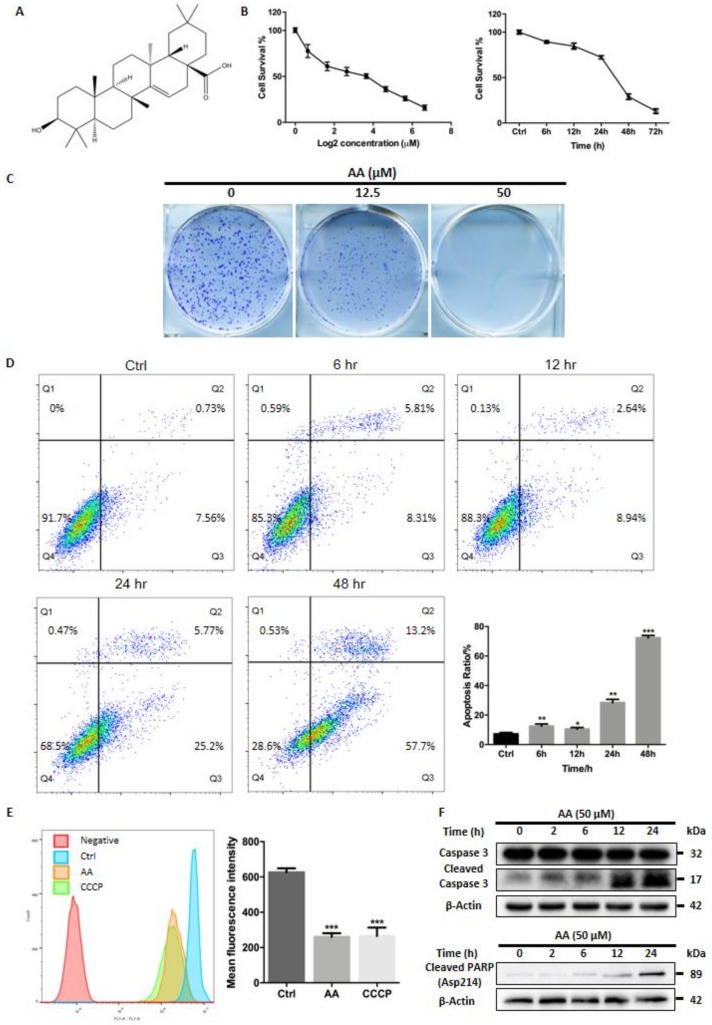
Figure 1.
AA exhibited cytotoxic effects against HepG2 cells. (A) The molecular structure of aleuritolic acid is shown. (B) MTT assay shows that AA caused dose-dependent and time-dependent inhibitory effects on growth of HepG2 cells. The IC50 is 10.2 μM. (C) Colony formation assays demonstrated a dose-dependent inhibitory effect of AA on colony formation of HepG2 cells. (D) AA treatment for different times induced early and late apoptosis in HepG2 cells. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, One-way ANOVA. (E) AA treatment depolarized mitochondria in HepG2 cells. The effect was comparable with CCCP, an uncoupler of mitochondrial respiration. *** p < 0.001, One-way ANOVA. (F) AA treatment caused a time-dependent accumulation of cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved PARP (Asp214).