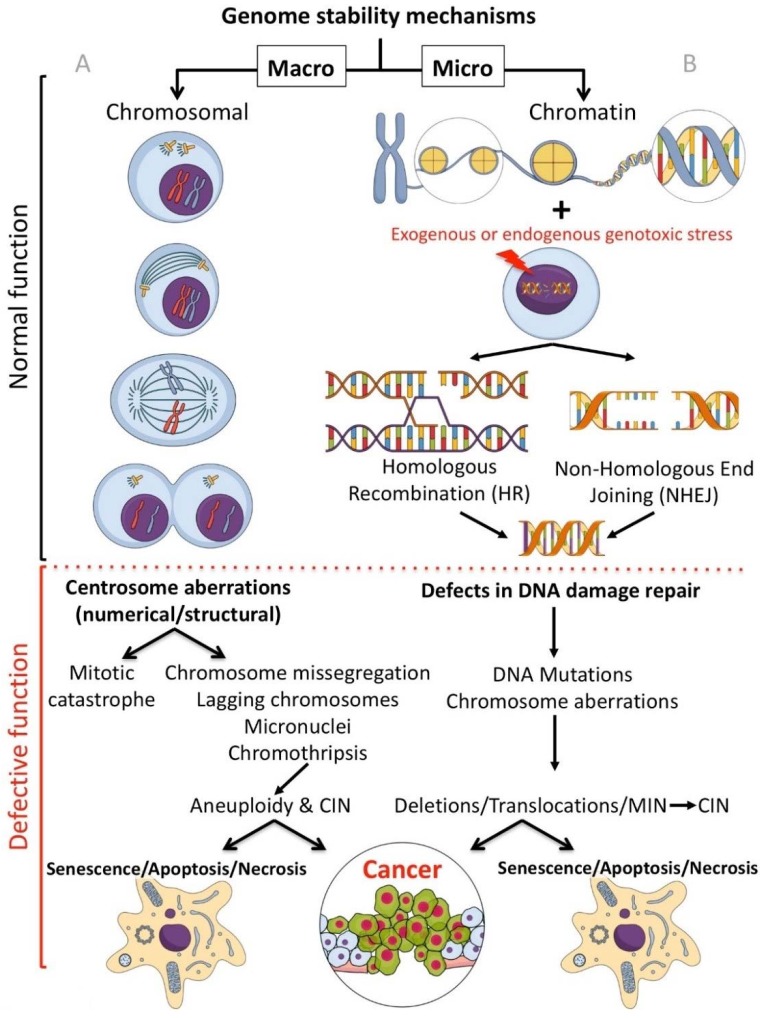
Figure 1.
Genome stability mechanisms. (A). Macro—chromosomal integrity protected by centrosomal pathways. CIN: chromosomal instability. (B). Micro—DNA damage response mechanisms protecting chromatin from DNA double strand breaks. Homologous Recombination (HR) utilizes the undamaged DNA template (through strand invasion) allowing faithful reproduction of the original sequence. Non-Homologous End Joining (NHEJ) modifies and re-ligates broken DNA ends without consideration of the original sequence, generating mutations (deletions or insertions). MIN: microsatellite instability.