Figure 4.
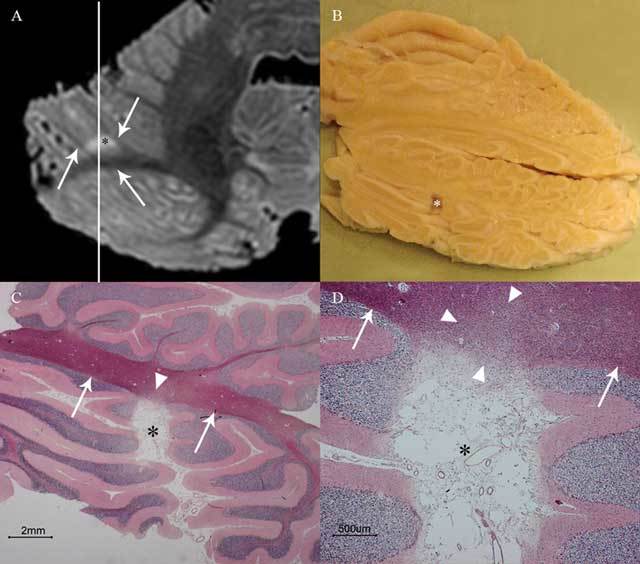
This image shows cerebellar cortical infarct cavity (asterisk) in the right cerebellar hemisphere on post-mortem 7T MRI (A; axial T2WI), gross specimen cut along the line indicated in A (B), and microscopy (C–D; HE stain). Notice the destruction of all three cortical layers on microscopy (C–D) and a preserved juxtacortical white matter (arrows in A, C, and D) with some microscopic gliotic changes (arrowheads in C and D). The surroundings of the cerebellum are dark on T2WI because the specimens were submerged in Fomblin (A), which does not yield MRI signal. Reproduced from Cerebrovascular Diseases [6].
