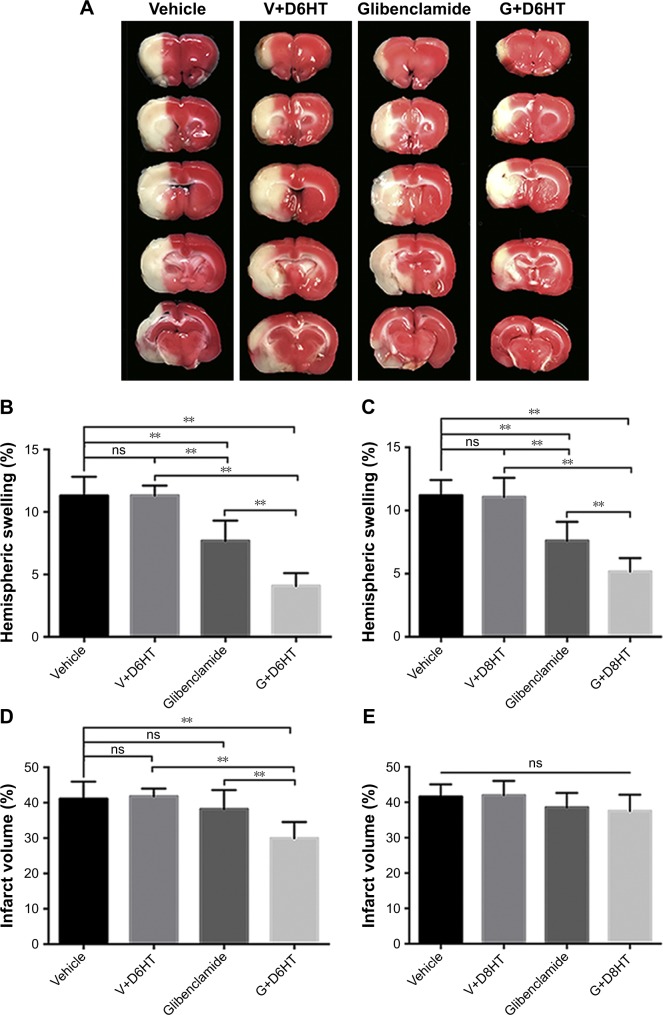
Figure 2.
Glyburide extends the therapeutic window for hypothermia and enhances its ability to attenuate cerebral edema and decrease infarct volume.
Notes: Rats were subjected to hypothermia or not at 6 or 8 hours after ischemia onset and rewarmed slowly at 0.5°C/h. (A) Representative triphenyltetrazolium chloride-stained coronal sections of rat brains at 24 hours after MCAo with treatments begun at 6 hours, as indicated, for vehicle only, vehicle combined with hypothermia at 6 hours after ischemia onset (V+D6HT), glyburide only, or glyburide with hypothermia at 6 hours after ischemia onset (G+D6HT). (B, C) Hemispheric swelling was compared among animals treated at 6 hours (B) or 8 hours (C). (D, E) Infarct volume was compared among animals treated at 6 hours (D) or 8 hours (E); **P<0.01. Copyright © 2003. Europe PMC. Adapted from Wu Z, Zhu SZ, Hu YF, et al. Glibenclamide enhances the effects of delayed hypothermia after experimental stroke in rats. Brain Res. 2016;1643:113–122.45
Abbreviations: MCAo, middle cerebral artery occlusion; ns, no significance.