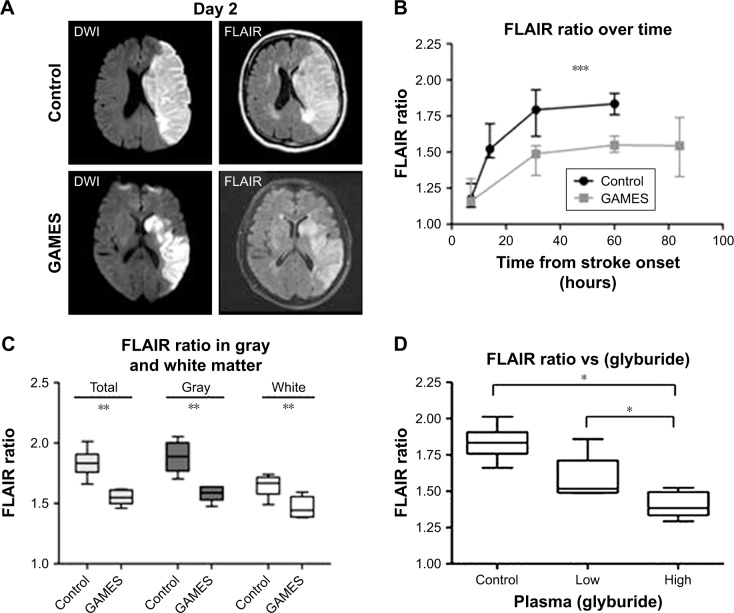
Figure 3.
Vasogenic edema on T2 FLAIR is attenuated by glyburide treatment in human stroke.
Notes: (A) Representative examples of DWI (left) and FLAIR sequences (right) from a control subject (top panels) and an RP-1127-treated subject (bottom panels); MRI scans were obtained at day 2 from the onset of stroke. (B) Quantitative analysis of the FLAIR ratio in control and GAMES-Pilot subjects shows a reduced FLAIR ratio with RP-1127 treatment; ***P<0.005 by repeated measures MANOVA. (C) Segmentation of the stroke lesions demonstrates an equivalent effect of RP-1127 on both gray and white matter regions; **P<0.01. (D) The plasma concentration of glyburide correlates with FLAIR ratio intensity in the GAMES-Pilot subjects; *P<0.01. Reprinted by permission from Springer Nature: Neurocrit Care. Glyburide is associated with attenuated vasogenic edema in stroke patients. Kimberly WT, Battey TW, Pham L, et al. 2014;20(2):193–201.82
Abbreviations: DWI, diffusion-weighted imaging; FLAIR, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery; MANOVA, multivariate analysis of variance; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.