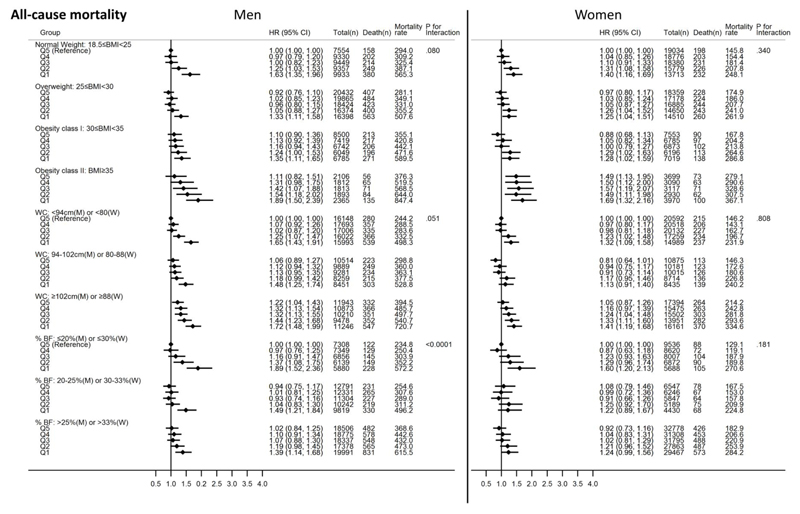
Figure 2.
Joint associations of grip strength and body mass index, waist circumference or percent body fat with all-cause mortality for men and women. All Cox regression models (using age as the underlying time variable) were adjusted for ethnicity (White, mixed, Asian/Asian British, Black/Black British, others), smoking status (never, previous, current), employment (unemployed, employed), Townsend Deprivation Index, statin use (yes/no), hormone replacement therapy (yes/no; women only), alcohol consumption (never, previous, currently <3times/week, currently ≥3times/week), processed/red meat consumption (days/week), resting pulse rate (beats/min), and moderate-to-vigorous physical activity time (minutes/day). The quintiles of grip strength were gender- and age-specific. Mortality rate is crude mortality rate per 100,000-person years. Cases with BMI<18.5 (n=369 for men; n=1,525 for women) were excluded in the models with BMI. Abbreviations: HR – hazard ratio; CI – confidence interval; M– men; W– Women.