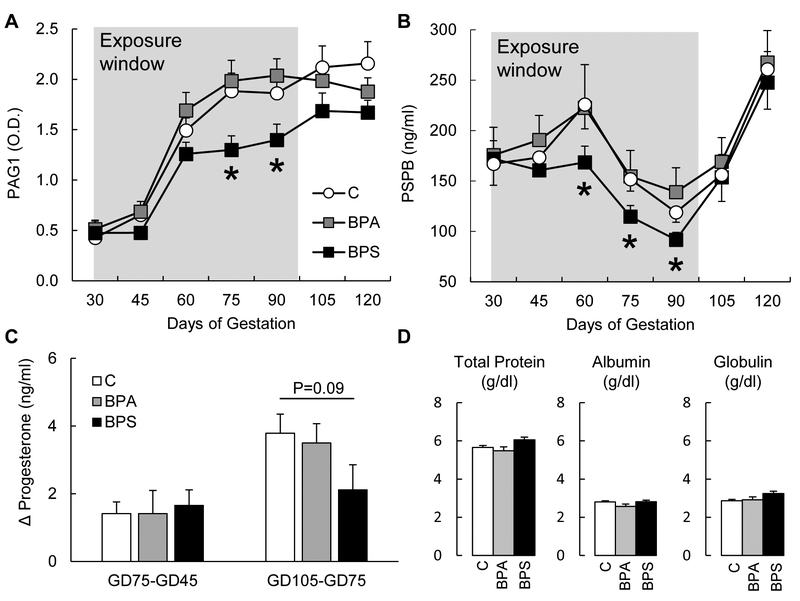
Figure 1.
Maternal serum (mean ± SE) pregnancy associated glycoprotein 1 (PAG1; (A)) and pregnancy specific protein B (PSPB (B)) in control (open circles), BPA- (gray squares) and BPS- (closed squares) exposed females. Change in maternal serum progesterone between GD45 and GD75 and between GD75 and GD105 (C) in control (open bars), BPA- (gray bars) and BPS- (closed bars) exposed females. Maternal serum (mean ± SE) total protein, albumin, and globulin at GD75 (D) in control (open bars), BPA- (gray bars) and BPS- (closed bars) exposed females. N=6–7/group. Asterisks denote statistical differences between control and BPS-exposed group at P<0.05.