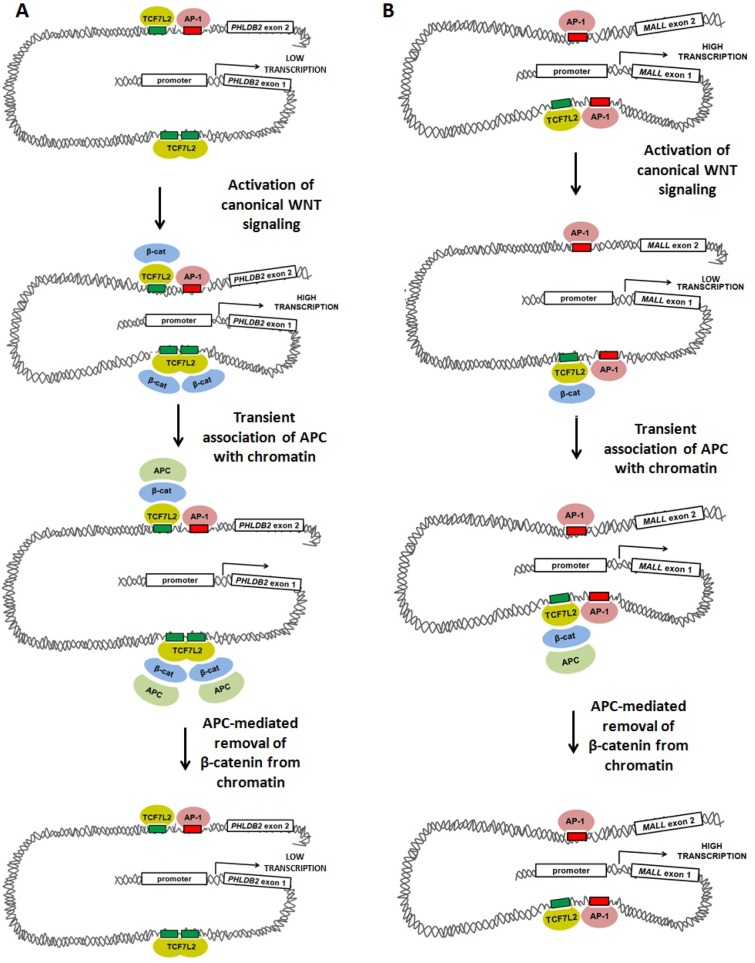
Figure 7. Models of WNT-mediated transcriptional activation and repression involving TCF7L2, AP-1, β-catenin and APC.
Our data suggest at least two models in which canonical WNT-mediated transcriptional activity, APC and AP-1 alter gene expression. (A) Activation of canonical WNT signaling up-regulates transcription of PHLDB2 through a previously-characterized mechanism in which β-catenin binds to the TCF7L2 transcription factor, promoting DNA bending that brings transcriptional machinery (including AP-1) into closer association with the proximal promoter. APC disrupts this association by mediating the removal of β-catenin from the complex. (B) Activation of canonical WNT signaling may down-regulate AP-1-dependent transcription of MALL through a mechanism in which β-catenin binding to TCF7L2 disrupts interaction of transcriptional machinery with the proximal promoter. APC may relieve this disruption by removing β-catenin from the complex.