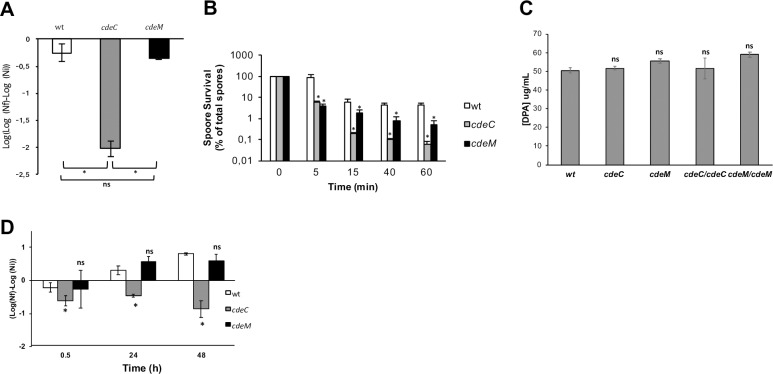
Fig 5. Absence of CdeC and CdeM renders C. difficile spores susceptible to ethanol, heat and macrophages.
(A) Ethanol 50% resistance of wild-type (white bar), cdeC (gray bar) and cdeM (black bar) spores. (B) Heat resistance of C. difficile wild-type (gray white), cdeC (gray bars), and cdeM (black bars) spores was measured by heat treating aliquots at 75°C for various times, and survivors were enumerated as described in the Material and Method section. (C) Equal amounts of spores derived from C. difficile strains 630erm (wt), cdeC, cdeM, cdeC/cdeC and cdeM/cdeM were boiled 60 min, and the amount of DPA was quantified based on Tb3+. The data shown represent the average results from three independent experiments, and the error bars represent standard error from the means. n.s., indicates no significant difference relative to wild-type. (D) Resistance of Raw 264.7 macrophages was determined by infecting at a MOI of 10 with C. difficile 630erm wild-type, cdeC and cdeM after 0,5, 24 and 48 of incubation at 37°C. Asterisks (*) denote statistical difference at P < 0.01 respect to wild-type.