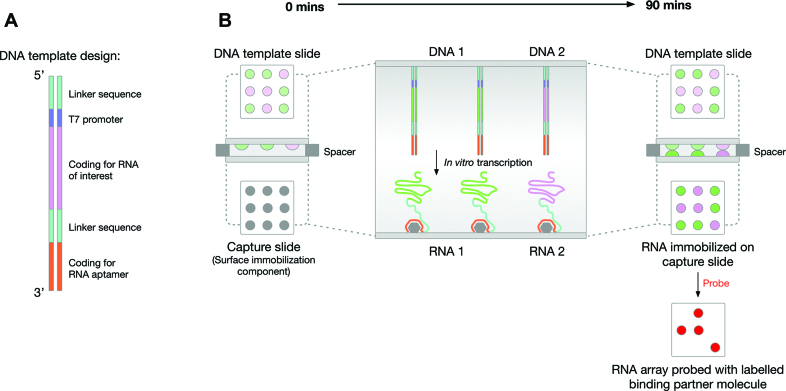
Figure 1.
Overview of functional-RNA array production. (A) The general design of the DNA in vitro transcription templates. From 5′ to 3′ there is: a short, biotinylated linker (to facilitate surface-immobilization of the DNA), a T7 promoter, sequence encoding the RNA of interest, a second linker (to separate the RNA of interest and the RNA aptamer) and sequence encoding an RNA aptamer (to facilitate RNA-capture). (B) A schematic representation of the ‘sandwich’ assembly and method used to produce the RNA array. A DNA in vitro transcription template array slide is positioned facing an RNA capture slide. Thin spacers are used to physically separate the surfaces. A solution of in vitro transcription reagents is inserted between the two surfaces and RNA transcription-capture proceeds for 90 min at 37°C to generate a functional-RNA array. This RNA array can then be used as a platform for investigating RNA-based interactions, e.g. probing with labelled binding partners.