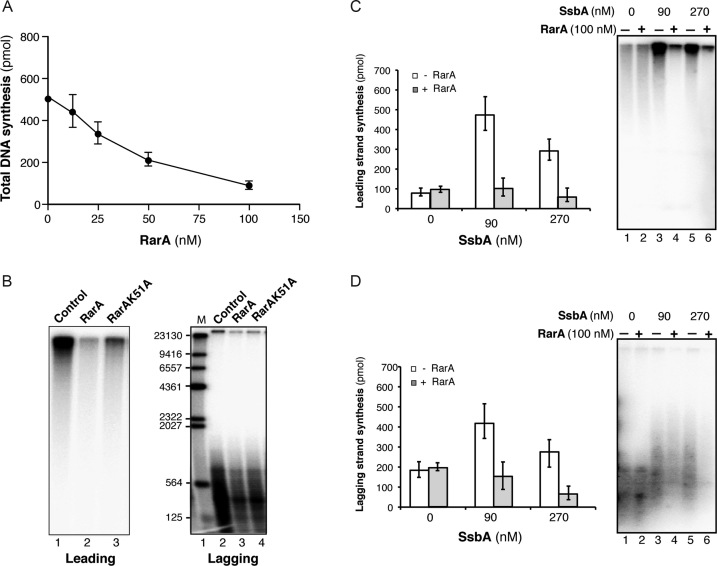
Figure 3.
SsbA-dependent RarA-mediated inhibition of B. subtilis PriA-dependent DNA replication. (A) Total DNA synthesis obtained in the presence of increasing RarA concentrations (15 min, 37°C). Reaction mixes contained all replisome components (preprimosomal proteins [PriA, DnaB, DnaD, DnaI), DnaC, DnaG, SsbA, τ-complex, β, PolC, DnaE), the indicated RarA concentration, template DNA, rNTPs, dNTPs and [α-32P]-dCTP and [α-32P]-dGTP. An enzyme mix consisting of all proteins except SsbA was generated and added to a substrate mix composed of template DNA, rNTPs, dNTPs, and SsbA. Then, samples were placed at 37°C. (B) Visualization of products obtained in the presence of 100 nM RarA or RarAK51A (15 min, 37°C). In the presence of [α-32P]-dCTP very large DNA fragments derived from rolling circle leading strand DNA synthesis is observed. A parallel reaction in the presence of [α-32P]-dGTP renders visible the small Okazaki fragments due to lagging strand DNA synthesis. Quantification of leading (C) and lagging strand (D) synthesis in the absence/presence of 100nM RarA and the indicated SsbA concentrations (15 min, 37°C). The quantification of the results is expressed as the mean ± SEM of six independent experiments. On the right part, a representative alkaline gel visualized by autoradiography showing the products of the DNA synthesis obtained in the presence or absence of RarA and SsbA.