Figure 1.
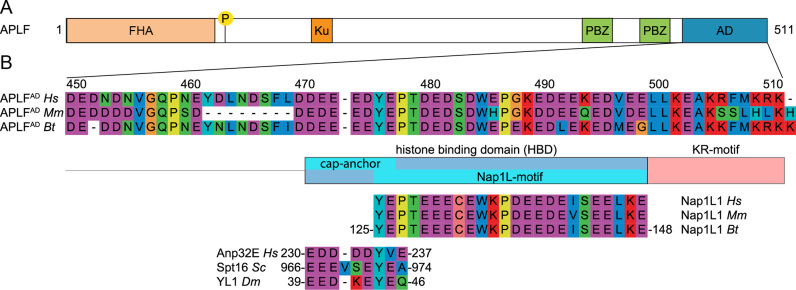
APLF contains an extended HBD in its acidic domain. (A) Schematic representation of the APLF domain architecture. FHA = Forkhead associated domain, P = phosphorylation site Ser116, Ku = Ku-binding motif, PBZ = Poly(ADP)ribose Binding Zinc finger, AD = acidic domain. (B) Sequence alignment of APLFAD, motif analysis and alignment with histone chaperones. APLFAD shows conservation among species and with two motifs from histone chaperones: the NAP1L-motif present in Nap1-like proteins and the H2A-H2B binding cap-anchor motif of histone chaperones Anp32E, Spt16 and YL1. The amino acids are displayed by Seaview with color coding according to amino acid properties. Abbreviations: Hs = Homo sapiens; Mm = Mus musculus; Bt = Bos taurus; Sc = Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Dm = Drosophila melanogaster.