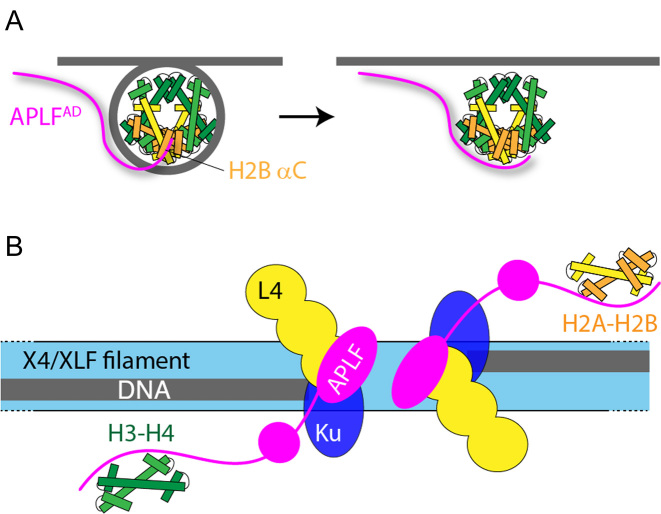
Figure 9.
Schematic model of APLF chaperone function in NHEJ. (A) APLF binds to the nucleosome via its acidic domain to the H2B αC helix. After nucleosome disassembly, a conformational rearrangement leads to APLF binding to the DNA binding surface of the histones to prevent non-nucleosomal interactions and store the core histones. (B) Schematic model of the NHEJ complex, based on ref. (13) and this work. Broken DNA strands are held in place by the XRCC4 (X4)/XRCC4-like factor (XLF) protein filaments. The DNA ends are bound by Ku and DNA ligase IV (L4). APLF is bound to X4/L4 via its FHA domain at the DNA break site and stores core histone complexes for later reassembly of nucleosomes. Color coding: gray—DNA; green—H3-H4; yellow/orange—H2A-H2B.