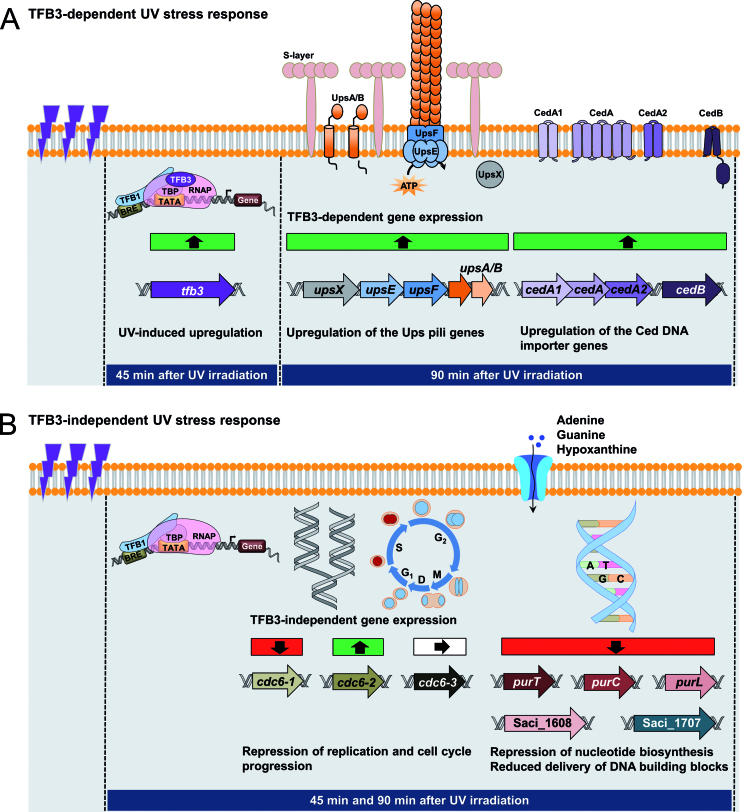
Figure 7.
Model of early UV stress response in Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. The increased and decreased transcription of genes is depicted by green and red squares, respectively, while white squares represent unchanged transcription. (A) TFB3-dependent UV stress response. 45 min after UV irradiation (100 J/m2), tfb3 is highly up-regulated and acts as an activator of transcription. The delayed (90 min after UV irradiation) response includes the enhanced transcription of the tfb3-dependent target genes (ups genes of the UV inducible pili operon, ced genes of the Crenarchaeal Exchange of DNA importer), leading to increased cellular aggregation and DNA exchange between the cells in order to allow DNA repair via homologous recombination. (B) TFB3-independent response. Apart from the TFB3-dependent response, S. acidocaldarius shows a UV stress response (45 and 90 min after UV irradiation), which does not depend on the presence of TFB3. This is characterized by the repression of DNA replication and cell cycle progression as well as the inhibition of nucleotide biosynthesis, leading to reduced delivery of DNA building blocks. Downregulation of these processes allow the DNA repair, which is mediated by the TFB3-dependent features described above to take place. For detailed discussion see text.