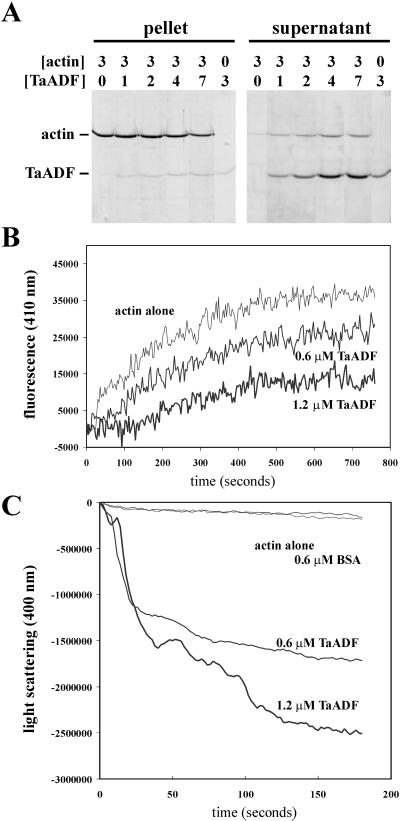
Figure 2.
TaADF is an active ADF. Purified actin and TaADF were used at the indicated concentrations (micromolars) in the different assays. A, Cosedimentation assays. F-actin and TaADF were mixed and incubated, and then polymerized actin was pelleted. The pellet and supernatant fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. B, Actin nucleotide exchange assays. The interaction of TaADF with G-actin ATP was determined by the inhibition of actin nucleotide exchange using etheno-ATP (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR) and fluorescence detection. C, Actin depolymerization assays. F-actin depolymerization by TaADF was followed by the decrease of light scattering at 400 nm. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) was used as a negative control.