Figure 1.
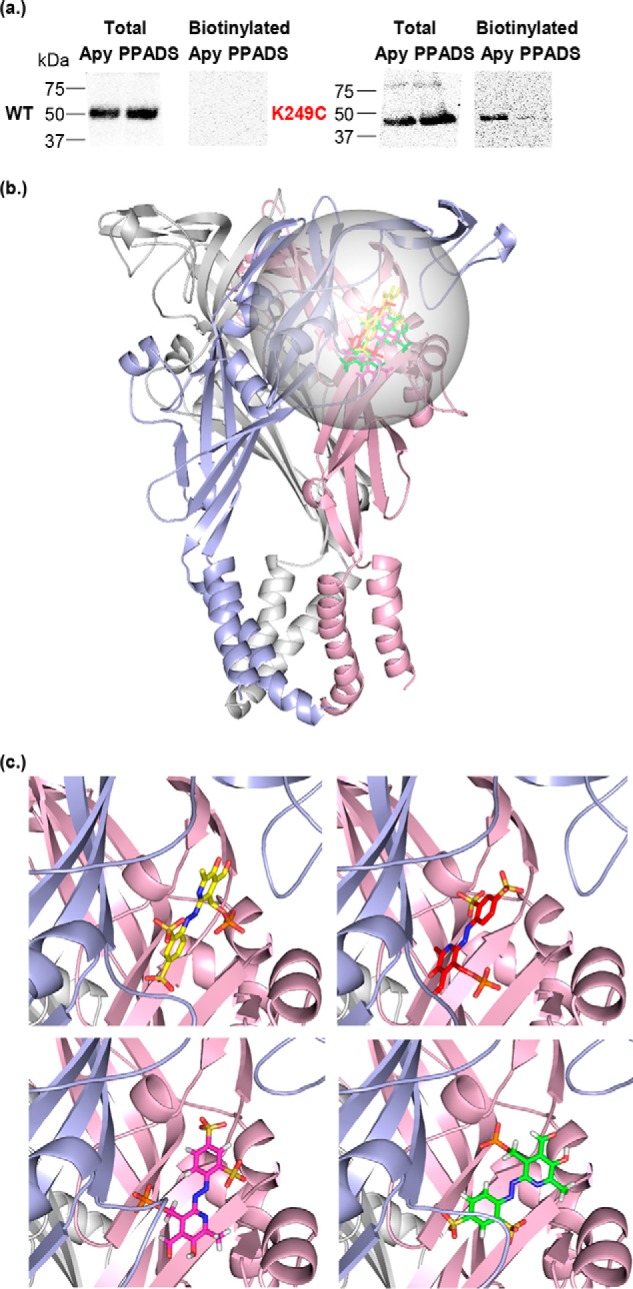
Access to the K249C hP2X1R mutant is reduced by PPADS binding and was the starting point for RosettaLigand docking. a, representative blots of MTSEA-biotinylation of hP2X1 receptor WT and the K249C mutant. Oocytes were treated with apyrase (Apy, 15 units/ml) or apyrase + PPADS (100 μm). Data show expression of the P2X1 in the total samples, however, biotinylation of the WT receptor was below the limit of detection. The K249C mutant receptor was biotinylated and this was reduced by PPADS treatment. b, PPADS docked into both, apo and open state hP2X1R models (for clarity only the open state receptor is shown). Individual subunits are colored in blue, pink, and gray. Docking was focused on the extracellular region centered at Lys-249, the sampled space is indicated by a transparent sphere. Representative docked ligands of the top ranking clusters for open and apo states are shown as sticks. c, zoom into b, representative docking solutions of top ranking clusters for hP2X1R apo state models (bottom) and hP2X1R open state models (top). These clusters were further analyzed for agreement/disagreement with the experimental data presented in this work.
