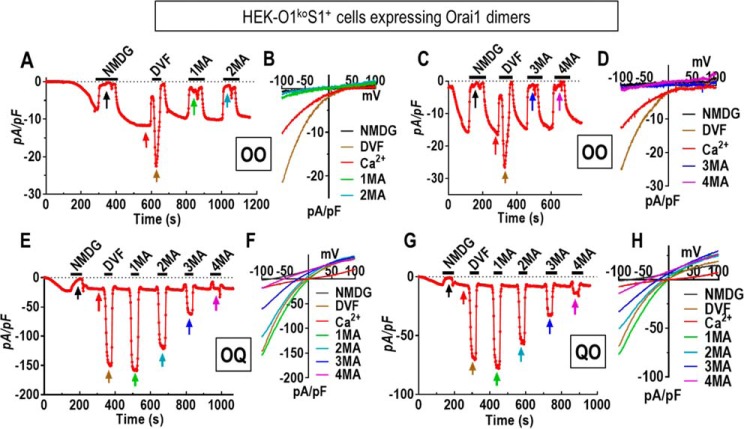
Figure 5.
Altered pore properties of the nonselective Orai1 concatenated channel dimers OQ and QO. A–D, electrophysiological measurements using HEK-O1koS1+ cells expressing the Orai1-WT dimer (OO). Current developed initially in the presence of 20 mm Ca2+ in the external solution. Thereafter, the external solution was periodically switched from 20 mm Ca2+ with 130 mm Na+ to divalent cation-free solutions containing the following: 150 mm N-methyl-d-glucamine (NMDG), 150 mm Na+ (DVF), 150 mm methylammonium (1MA); 150 mm dimethylammonium (2MA); 150 mm trimethylammonium (3MA); and finally 150 mm tetramethylammonium (4MA). Between each divalent-free addition, cells were switched back to 20 mm Ca2+ with 130 mm Na+. Current at −100 mV was plotted against time, and I/V relationships are shown (B and D) at the times indicated by arrows in A and C. E, using HEK-O1koS1+ cells expressing the OQ dimer, current developed in 20 mm external Ca2+. After switching to NMDG, divalent solutions were again added in the external solution as shown in A and C. For channel formed by OQ heterodimers, methylated ammonium cation still can produce significant currents. F, I/V relationship of currents mediated by OQ collected in different external solutions as indicated by the arrows in E. G, HEK-O1koS1+ cells expressing the QO dimer were exposed to external solutions as shown in E. H, I/V relationship of currents mediated by QO collected in the external solutions indicated in G.