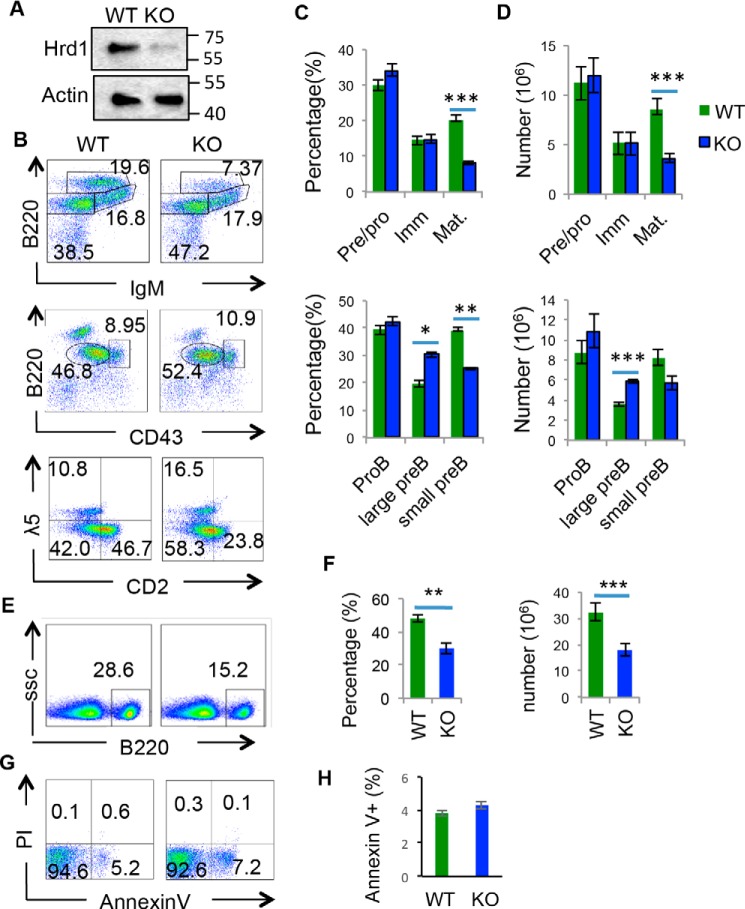
Figure 1.
Deletion of Hrd1 leads to a developmental block at the large pre–B cell stage and reduced viability of immature and mature B cells. A, B220+ cells were isolated from bone marrow of WT and Hrd1 KO (KO) mice and immunoblotted for Hrd1 protein. β-Actin protein served as loading control. B, bone marrow isolated from WT and Hrd1 KO (KO) mice was analyzed for B220LOIgM− pro–B and pre–B cells, B220LOIgM+ immature B cells, and B220HIIgM+ mature B cells (top panel). B220LOIgM− populations were further analyzed for B220+CD43HI pro–B and B220+CD43LO pre–B cells (middle panel). B220LOIgM− cells were also analyzed for CD2− icλ5− pro–B, CD2− icλ5+ large pre–B, and CD2+ icλ5− small pre–B cells (bottom panel). C, percentages of B cell development stages by B220 and IgM gating (top panel) and icλ5 and CD2 gating (bottom panel). D, absolute number of B cell stages as analyzed in B. E, splenic B cell populations in WT and KO mice were analyzed by B220 expression. F, percentages (left) and absolute number (right) of B220+ cells in spleen. G, bone marrow B cells from WT and KO mice were cultured in media for 4 h and the apoptosis of B220lowIgM− pre/pro–B cells were analyzed by Annexin-V and propidium iodide staining. H, quantification of apoptosis as analyzed in G. Error bars represent S.D. n = 10. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.