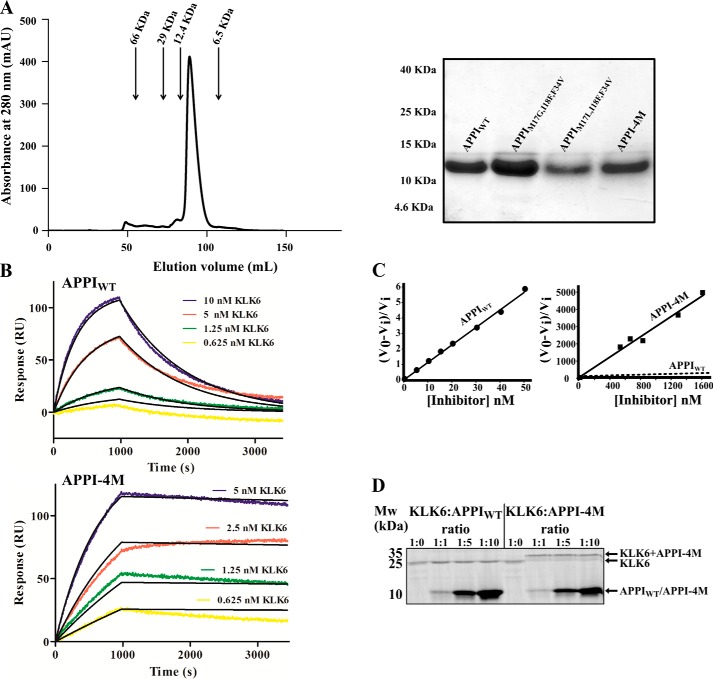
Figure 3.
Binding and inhibition kinetics of KLK6 by APPIWT and APPI-4M. A, purification of soluble APPI variants. Left, size-exclusion chromatography for APPI-4M. Arrows indicate correlations between the elution volume and size, according to known standards. Right, SDS-PAGE analysis of the purified APPI variants on a 15% polyacrylamide gel under reducing conditions. B, surface plasmon resonance binding experiment, in which 2 μg of either APPIWT (top panel) or APPI-4M (lower panel) was mounted as the ligands on a GLC chip. Six KLK6 concentrations (0–10 nm; represented by different colors) were used as the analytes. C, slow tight–binding inhibition of KLK6 catalytic activity by APPIWT (left, 1 nm KLK6) and APPI-4M (right, 100 nm KLK6). The Ki value of the reaction was calculated by using Equation 1 (see under “Experimental procedures”). V0 represents the uninhibited rate, and Vi represents the rate in the presence of APPI. In the APPI-4M plot, the dashed regression line indicates the slope of the inhibition by APPIWT. D, formation of complexes between KLK6 and APPI-4M. The SDS-PAGE was performed under reducing conditions and with KLK6/APPI molar ratios of 1:0, 1:1, 1:5, and 1:10. Note the formation of stable, higher molecular weight complexes in lanes loaded with KLK6/APPI-4M but not with KLK6/APPIWT complexes.