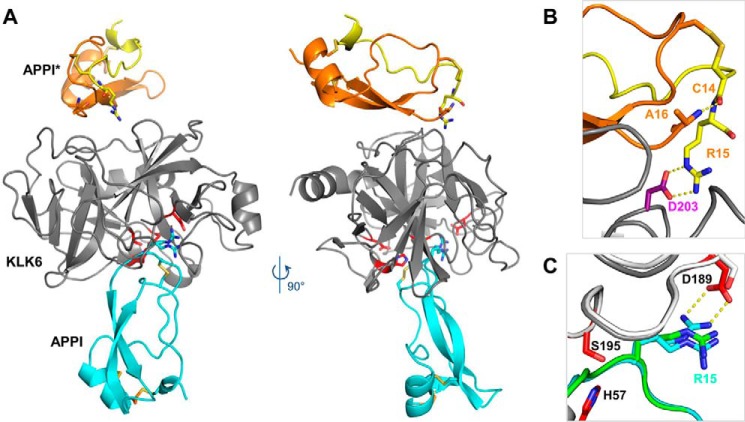
Figure 6.
Crystal structure reveals an inhibited KLK6/APPI-4M complex and a cleaved product APPI-4M*. A, co-crystal structure of KLK6 with the APPI-4M variant shows one molecule of KLK6 (gray) bound to a molecule of APPI-4M occupying the active site in the inhibitory mode (cyan). The crystal structure also reveals an additional APPI-4M molecule that has undergone proteolysis at Arg-15–Ala-16 to yield the product APPI-4M*, which is comprised of two protein chains (yellow and orange) connected by two disulfide bonds. B, cleaved APPI-4M* molecule reveals a large rotation of the Cys-14 ψ angle (relative to the intact APPI-4M), allowing the formation of a salt bridge between the Arg-15 side chain and the Asp-203 residue of KLK6, thus stabilizing the crystal lattice, whereas the Cys-14 carbonyl forms a hydrogen bond with the Ala-16 N terminus. C, Arg-15 of the intact APPI-4M was observed in both the expected “up” conformation, in which it forms a salt bridge with KLK6 Asp-189 (dotted yellow lines), and a “down” conformation, which is similar to that previously reported in the superposed structure of APPI (green) bound to chymotrypsin (white) (PDB code 1CA0).