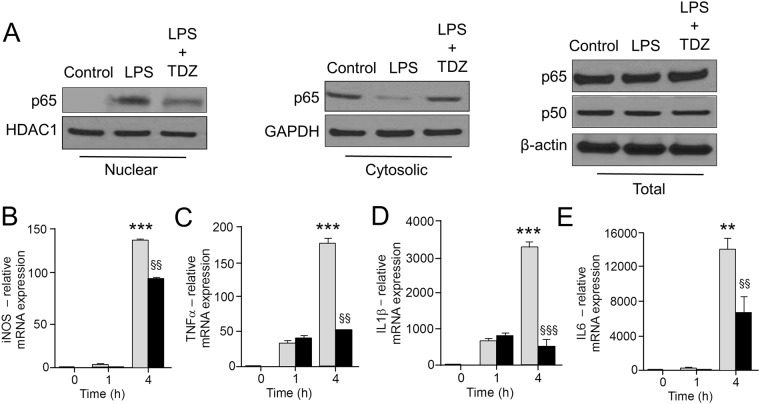
Figure 5.
TDZ inhibits NF-κB nuclear translocation and suppressed the induction of NF-kB dependent pro-inflammatory signatures in RAW 264.7 macrophages. (A) Isolated cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions were probed for p65 by immunoblot before and after LPS (250 ng/ml) for 15 min, GAPDH and HDAC1 are loading controls for cytoplasmic or nuclear protein, respectively. (B–E) qPCR quantification of NF-kB dependent genes including iNOS, TNFα, IL1β, and IL6 treated with LPS or LPS + TDZ for the indicated time. The treatment of macrophages with TDZ significantly suppressed the transcription of NF-kB dependent genes. Values were normalized to GAPDH. P values were determined by Student’s T-test; ***P < 0.005, <0.005**P < 0.05, §§<0.001.